What Is Smart Dust? Here's What You Need To Know
Every few years, a new technology comes around that the general public doesn't understand as well as its creators might like, such as artificial intelligence and the evolution of machine learning, which sparked concerns about all manner of end-of-the-world fiction. For the most part, technologies not designed for purely military use are relatively benign. This is true of everything from AI to a new technology making headlines, smart dust.
Smart dust isn't a single technological leap, nor is it a single machine. Instead, smart dust consists of incredibly small microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) that can carry out various tasks. They operate through wireless networks via a computer and are most commonly used as sensors. If that description makes you think it could be used as a nanotechnological nightmare scenario of so-called "Grey Goo" or other world-ending tech, you don't have anything to worry about, as smart dust is typically passive.
Smart Dust has a wide range of potential uses, and while the technology has been in development for some time, it won't be changing the world just yet. More work is needed to bring smart dust systems up to the level they need to be to work well and at a relatively low cost. To that end, research is being conducted to move the technology out of the conceptual stage and into practical use applications.
What exactly is smart dust
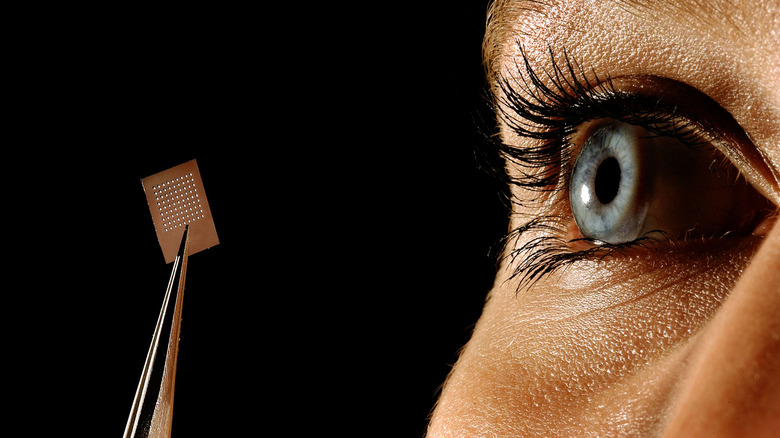
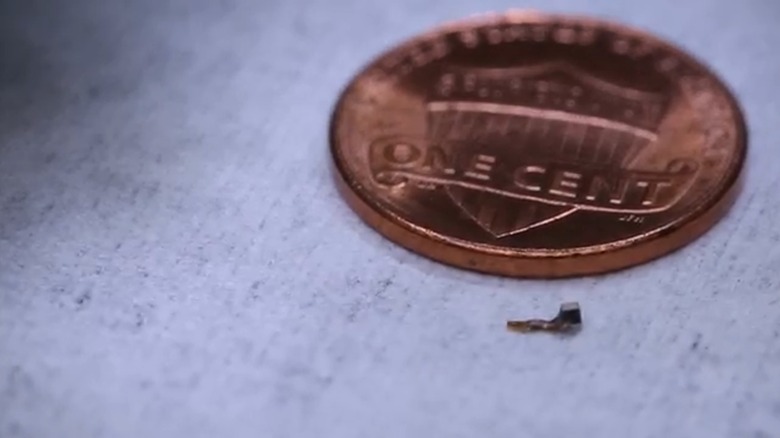
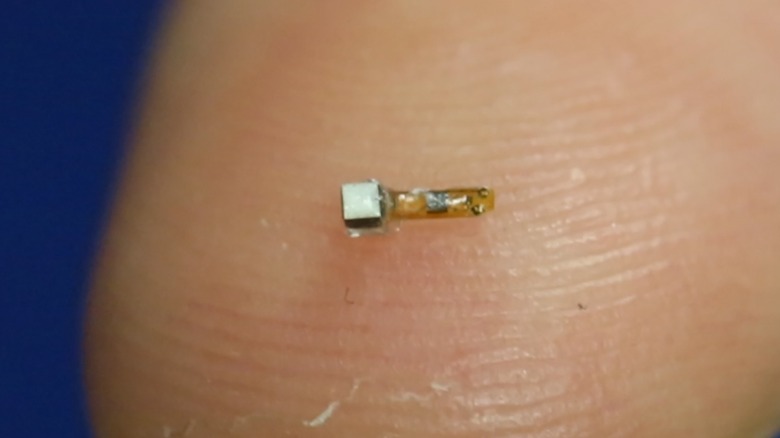
Smart dust is a classification for a system of incredibly small electromechanical sensors capable of detecting input and wirelessly transmitting it in real time. To be considered smart dust, a sensor must be measured at one cubic millimeter or smaller. This theoretically makes it possible for some smart dust sensors to be suspended in mid-air, like dust. Also, a whole bunch of them need to be active to function as desired.
They're constructed via 3D printers, primarily out of silicon, and weigh a few micrograms at the most, which is how they can remain suspended in the air for a time. Currently, smart dust sensors can perform a variety of tasks, including detecting temperature, sound, light, chemicals, air pressure, and movement in their immediate area. This information is relayed to a computer for analysis or for whatever purpose the smart dust has been tasked to perform.
Smart dust, as it exists now, is incredibly small, but it could be smaller. The technology is still in the early phases of development, and ideally, it can become truly minute. The goal is to make smart dust sensors via nanotechnology so they're literally the size of dust particles, which measure between .5 and 100 microns, or one billion times smaller than a one cubic centimeter sensor. Granted, it could be years before such a feat is achieved, if it's even possible with modern or burgeoning technology.
How can smart dust be used
There are near limitless ways smart dust can be used in civilian and military applications. This includes being utilized to monitor crops to determine the best uses of watering, pest control, and fertilization. They could also monitor equipment and provide information on maintenance needs, or they can detect corrosion before a system failure requires immediate action. On the more nefarious side, smart dust can monitor people, products, and places constantly across relatively large areas.
Smart dust can also be used for measurements, and by detecting everything from light to movement, it can measure all manner of things. MEMS could also help with inventory control to track products from the manufacturing process to putting items on store shelves. For healthcare, smart dust could be used for diagnostic purposes, ideally eliminating exploratory surgery in favor of detecting problems without having to be invasive to the patient.
Like any new technology, there are potential downsides, including the considerable cost of new technology like smart dust. There are also privacy concerns, as it would be all but impossible to shield oneself from billions of floating smart dust MEMS in their environment. This concern, along with others, has led some to fear the worst about smart dust, leading to conspiracy theories about the safety of the technology among a population.
Is smart dust the next step in Big Brother monitoring?
Because it's used to monitor the environment, people around the world have expressed concerns over the safety of smart dust. This has led to several conspiracy theories, many of which imagine the technology is far advanced beyond its current state.
In 2024, a large blanket of fog affected the United Kingdom and parts of North America. Some decided it was alien spores, while others believed it was some sort of chemical mist. Others settled on blaming smart dust as the culprit responsible for what folks were calling Fogvid-24. Some users on X, formerly known as Twitter, posted questions about smart dust, pointing to a patent the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) filed in the 1990s. Fogvid-24 sparked a worldwide interest in smart dust technology as many believed it was responsible for fogging up the northern hemisphere for a while.
In reality, smart dust is incapable of such a feat at this early stage of development. To envelop such a wide area, there would have to be trillions upon trillions of MEMS in the atmosphere, and that's a long way off. Of course, conspiracy theories rarely die even when presented with such information, so people are still concerned about smart dust and the dangers, especially to privacy, it represents. While it is possible that smart dust could be employed for nefarious monitoring means, the danger of that isn't something people need to worry about anytime soon.