Why You Should Always Enable 2-Factor Authentication
You've no doubt heard about two-factor authentication at some point in the relatively recent past, but if you're like many consumers, there's a good chance you haven't actually used it yet. If that's the case, it's time to learn about what, exactly, two-factor authentication is, how it works, and why it is very important that you use it.
What is two-factor authentication?
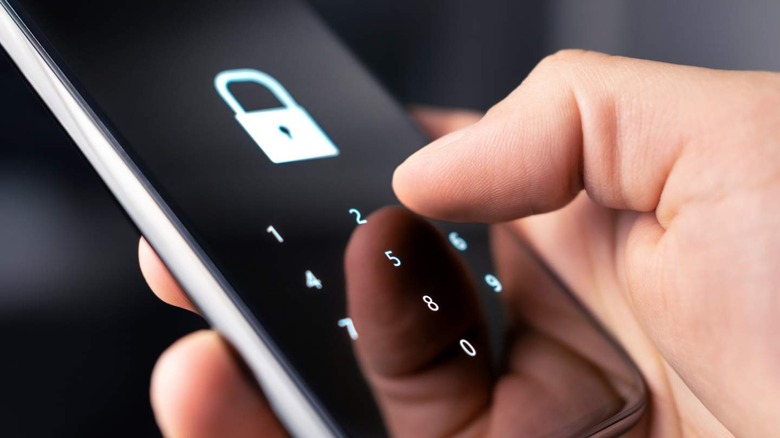
Put simply, two-factor authentication is an extra layer of security for your accounts that makes it much harder for intruders to access them (via Authy). The technology works by securing an account behind an authorization process that, typically speaking, revolves around the user's smartphone.
Accounts protected with two-factor authentication still require the user to sign in with their username and password. However, successfully entering those credentials won't provide access to the account. Instead, the user will then be prompted to complete the second authentication method (hence the term two-factor) in order to get past the security wall.
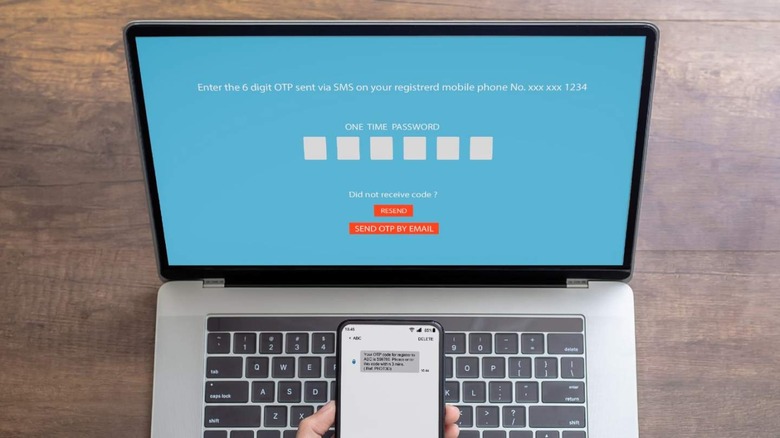
In most cases, two-factor authentication involves sending either a prompt to an app on the user's phone for them to tap, confirming that they're the person attempting to sign in, or by texting a code to their phone number that must be manually entered into the two-factor security prompt. The idea is that while someone may learn your username and password, they're not likely able to physically access your phone.
Different methods
Some two-factor authentication processes utilize an authenticator app instead of a text message. This is because, unfortunately, texting a sign-in code won't protect your account if you're the victim of a SIM swap attack (via PhishLabs). The most common version of a SIM swap attack involves calling the victim's wireless provider, pretending to be the account holder, and convincing the customer service agent to port the phone number over to the hacker.
An authenticator app, in comparison, is much harder to compromise, effectively locking the intruder out of the account. The apps work by scanning a QR code presented to the user when they turn two-factor authentication on in their account. Scanning the QR code links the account to the authenticator app, which generates a unique code that disappears and is replaced every minute or so.
The user will enter the code from the app into their account when signing in rather than getting the code in a text message. In other cases, an account may offer multiple authentication methods, addressing the biggest complaint consumers have about this extra layer of security: it's super inconvenient if you lose your phone.
Why you should use it
The days of being able to comfortably secure your accounts behind a username and password are over. Security breaches involving the theft of login credentials have become more common, and this information is often sold on the dark web to hackers and criminals interested in identity theft (via ID Agent). Once your credentials are leaked, anyone who has them can try and sign in to your account.
Two-factor authentication gives you more control over the entire process by limiting logins only to those who not only know the sign-in credentials, but who also have access to your phone (or, in some cases, email) to retrieve the correct code. Unless you're a high-profile individual, it's doubtful the average hacker will waste time trying to get past your two-factor authentication when there are other, less secure accounts they can target.