Intel Ivy Bridge Official: 22nm 3D Tri-Gate To Revolutionize Processors
Intel has announced its 22nm 3D Tri-Gate transistors, the world's first on a production technology, and with the potential to create not only smaller chips for smartphones, tablets and other ultraportables, but to make more powerful servers and desktop PCs. The 3D Tri-Gate transistors will be first used in Intel Ivy Bridge processors, demonstrated today and set to be the first high-volume CPUs based on the new technology. Intel isn't holding back on the hyperbole, saying Ivy Bridge will bring "an unprecedented combination of power savings and performance gains" – up to 37-percent more performance, in fact – and the company even managed to get Gordon E. Moore – who coined "Moore's Law" – to speak up on how important the 22nm evolution is to tech.
"For years we have seen limits to how small transistors can get. This change in the basic structure is a truly revolutionary approach, and one that should allow Moore's Law, and the historic pace of innovation, to continue" Gordon E. Moore
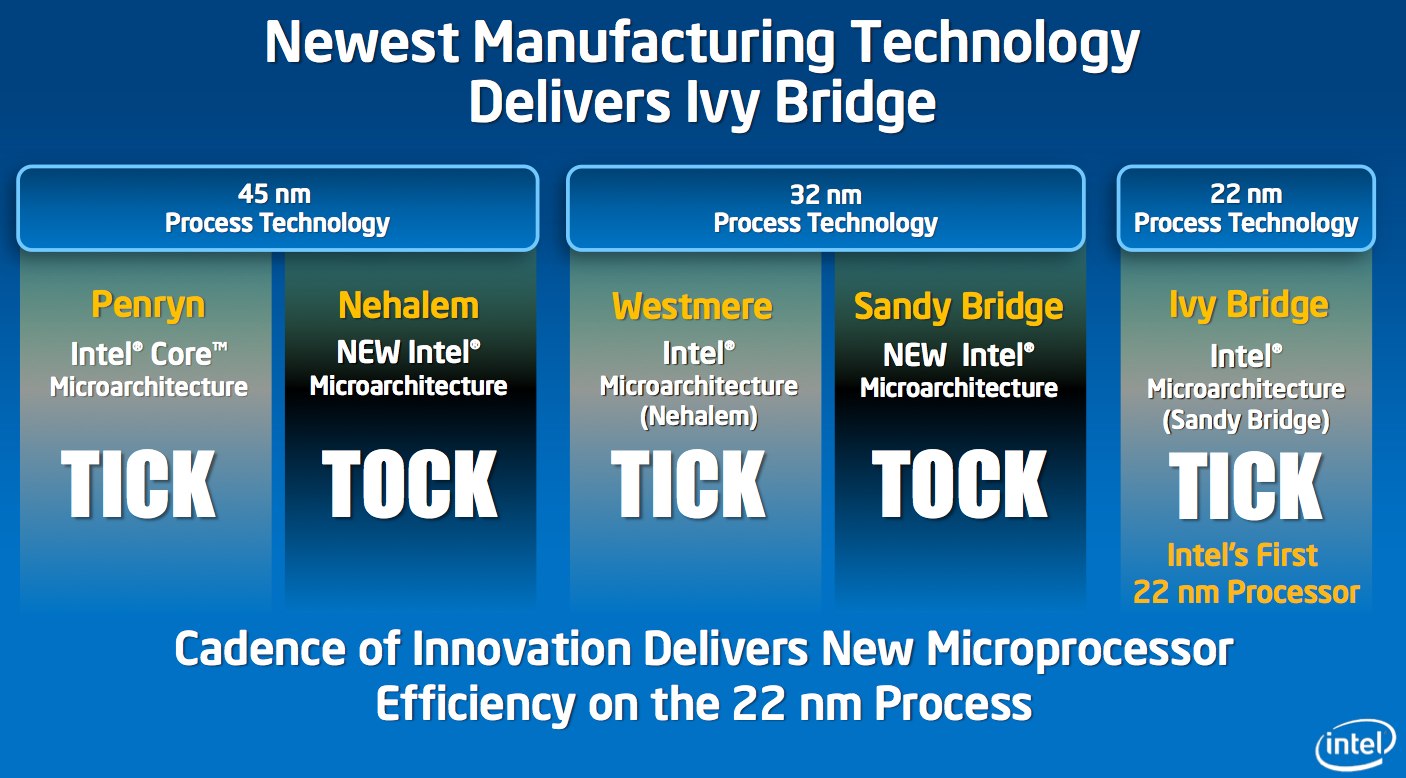
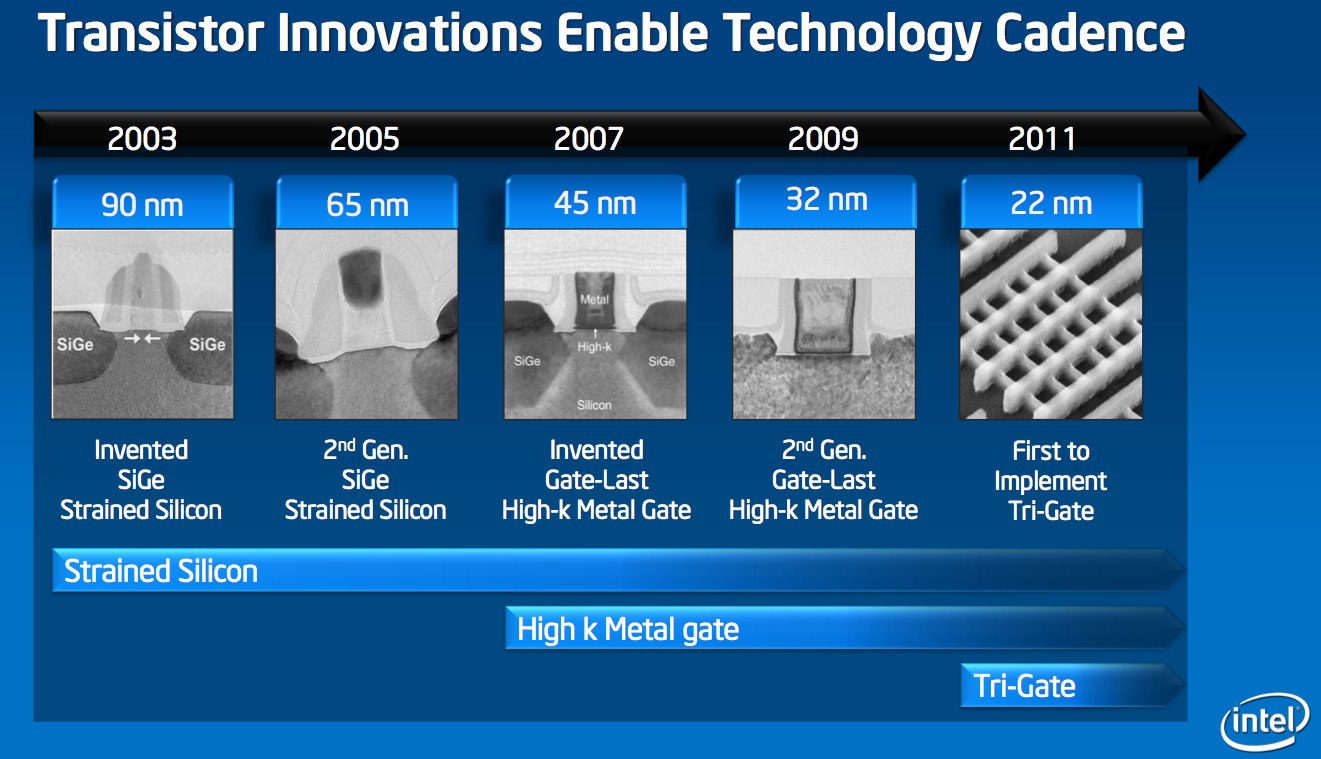
Intel's last significant production scale change took place in 2009, when the company shifted to 32nm processes. That was the second-generation of so-called High k Metal gate transistors, which originally debuted in 2007 with 45nm processes (and surplanted the Strained Silicon technology that had been in use since 2003).
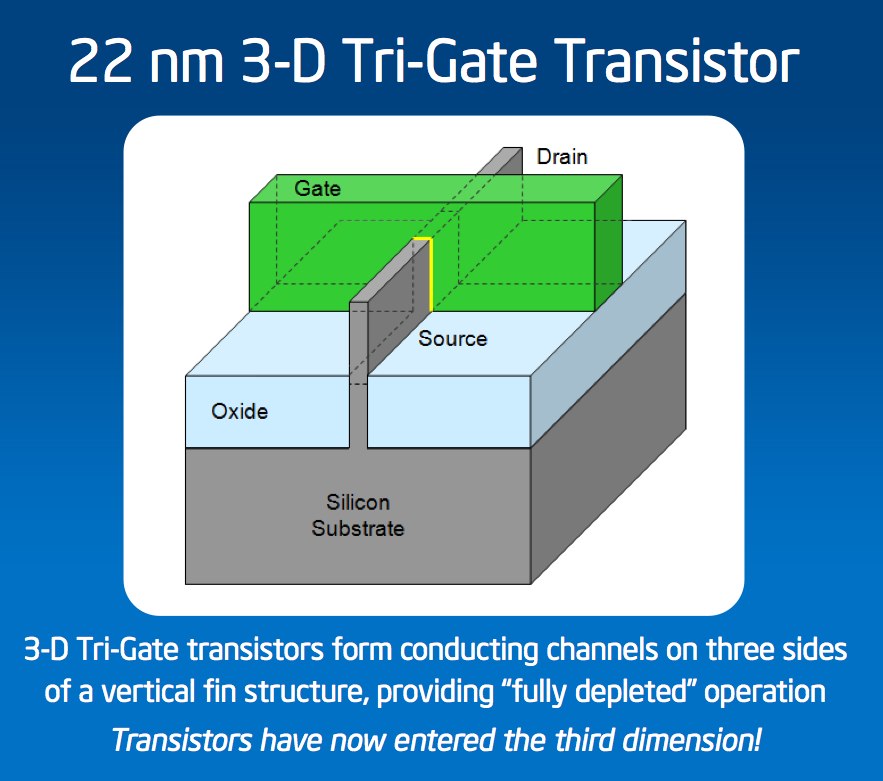
The "3D" in the name isn't just Intel attempting to cash in on the A/V industry's latest wheeze. In fact, the 3D Tri-Gate transistors form conducting channels on three sides of a "vertical fin structure"; Intel says this system – which it initially announced back in 2002 – results in less heat being given off, longer battery life for mobile devices, and improved performance thanks to the combination of high-k gate insulators and strained silicon.
"Tri-gate fully-depleted substrate transistors have a raised plateau-like gate structure with two vertical walls and a horizontal wall of gate electrode. This three-dimensional structure improves the drive current while the depleted substrate reduces the leakage current when the transistor is in the "off" state. Reducing leakage current not only helps control heat at the circuit level but also translates to increased battery life in mobile devices" Intel
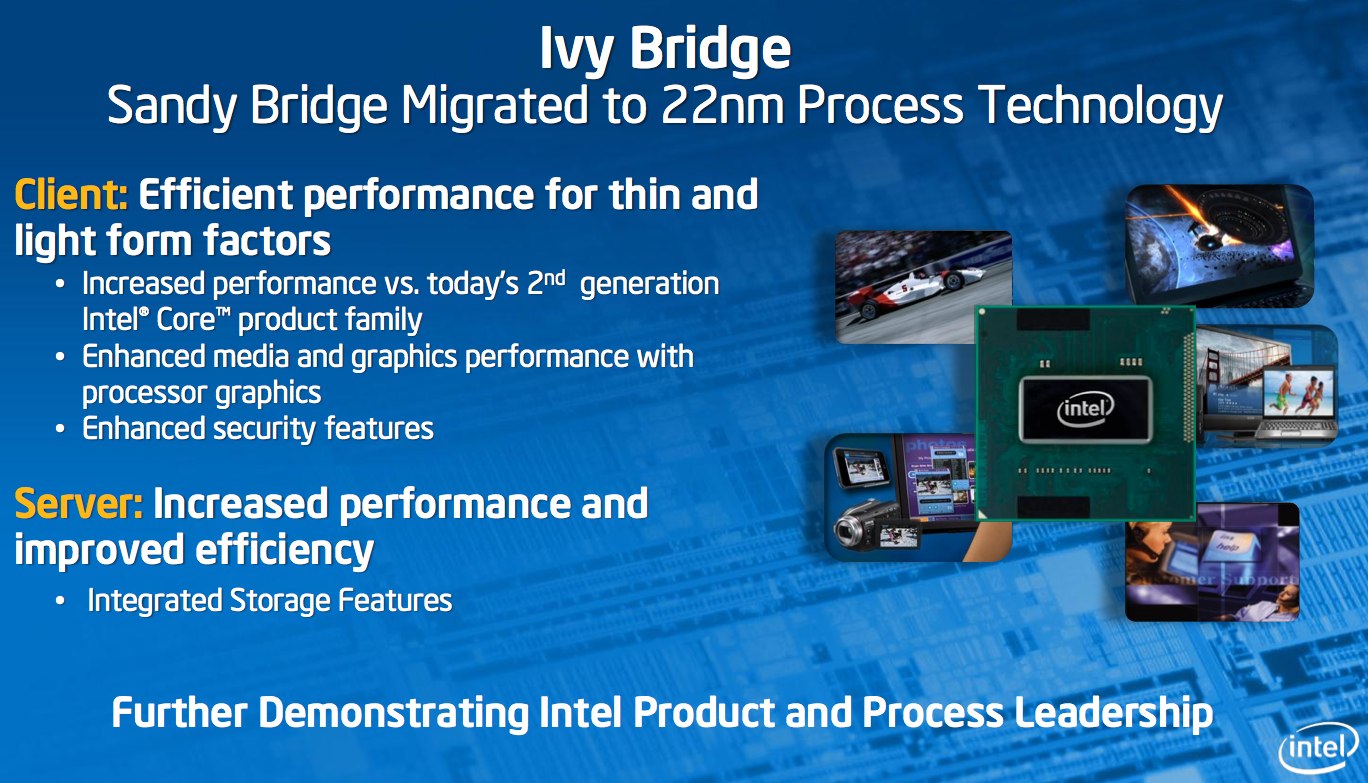
Intel Ivy Bridge will use similar architecture to the existing Sandy Bridge, the basis of the current 2011 Core processor range. There's expected to be native USB 3.0 and PCIe 3.0 controllers at the processor level, along with an integrated DirectX graphics core with support for the second-generation of QuickSync, Intel's media encoding/decoding acceleration technology. The first Ivy Bridge chips are expected to reach high-volume production readiness by the end of this year.
Press Release:
Intel Reinvents Transistors Using New 3-D StructureNew Transistors for 22 Nanometer Chips Have an Unprecedented Combination of Power Savings and Performance Gains
NEWS HIGHLIGHTS
Intel announces a major technical breakthrough and historic innovation in microprocessors: the world's first 3-D transistors, called Tri-Gate, in a production technology.
The transition to 3-D Tri-Gate transistors sustains the pace of technology advancement, fueling Moore's Law for years to come.
An unprecedented combination of performance improvement and power reduction to enable new innovations across a range of future 22nm-based devices from the smallest handhelds to powerful cloud-based servers.
Intel demonstrates a 22nm microprocessor – codenamed "Ivy Bridge" – that will be the first high-volume chip to use 3-D Tri-Gate transistors.
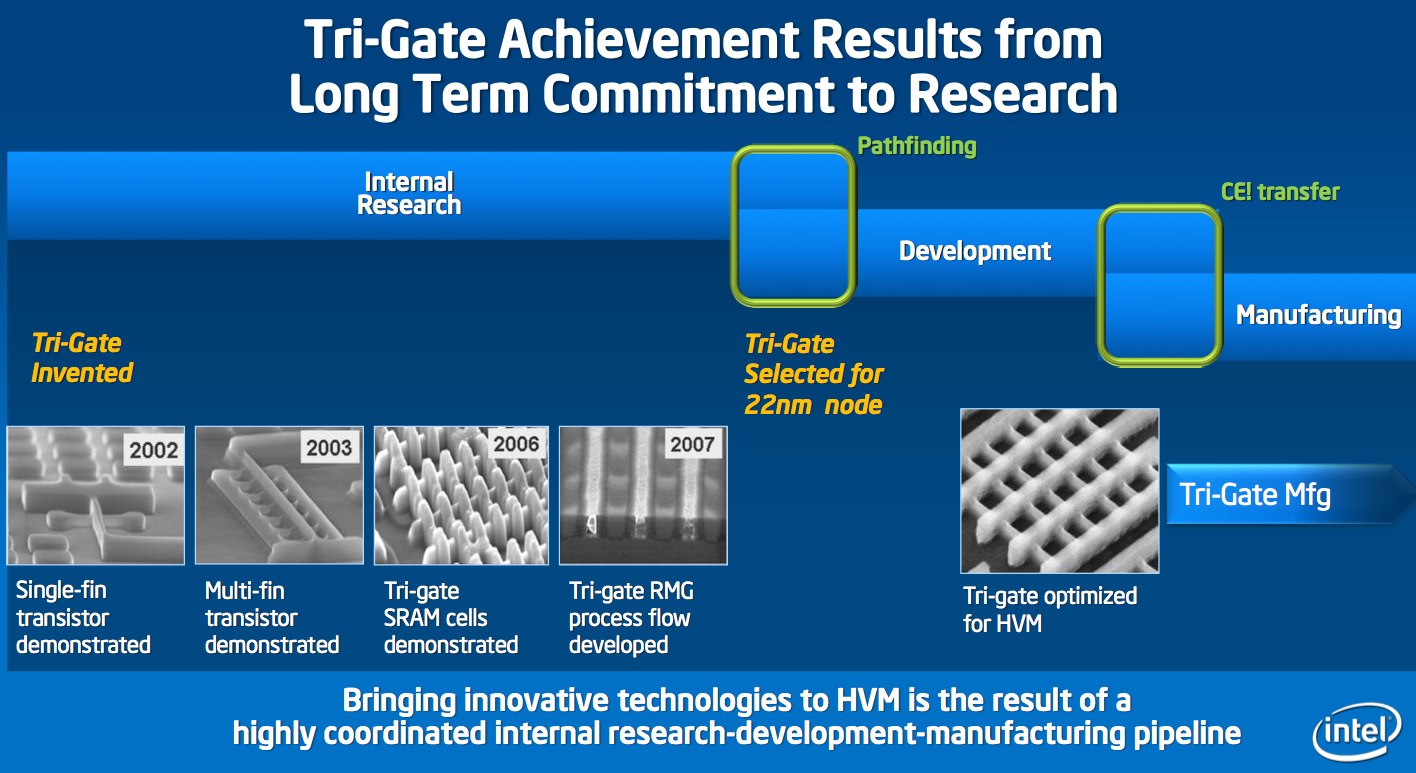
SANTA CLARA, Calif., May 4, 2011 – Intel Corporation today announced a significant breakthrough in the evolution of the transistor, the microscopic building block of modern electronics. For the first time since the invention of silicon transistors over 50 years ago, transistors using a three-dimensional structure will be put into high-volume manufacturing. Intel will introduce a revolutionary 3-D transistor design called Tri-Gate, first disclosed by Intel in 2002, into high-volume manufacturing at the 22-nanometer (nm) node in an Intel chip codenamed "Ivy Bridge." A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.
The three-dimensional Tri-Gate transistors represent a fundamental departure from the two-dimensional planar transistor structure that has powered not only all computers, mobile phones and consumer electronics to-date, but also the electronic controls within cars, spacecraft, household appliances, medical devices and virtually thousands of other everyday devices for decades.
"Intel's scientists and engineers have once again reinvented the transistor, this time utilizing the third dimension," said Intel President and CEO Paul Otellini. "Amazing, world-shaping devices will be created from this capability as we advance Moore's Law into new realms."
Scientists have long recognized the benefits of a 3-D structure for sustaining the pace of Moore's Law as device dimensions become so small that physical laws become barriers to advancement. The key to today's breakthrough is Intel's ability to deploy its novel 3-D Tri-Gate transistor design into high-volume manufacturing, ushering in the next era of Moore's Law and opening the door to a new generation of innovations across a broad spectrum of devices.
Moore's Law is a forecast for the pace of silicon technology development that states that roughly every 2 years transistor density will double, while increasing functionality and performance and decreasing costs. It has become the basic business model for the semiconductor industry for more than 40 years.
Unprecedented Power Savings and Performance Gains
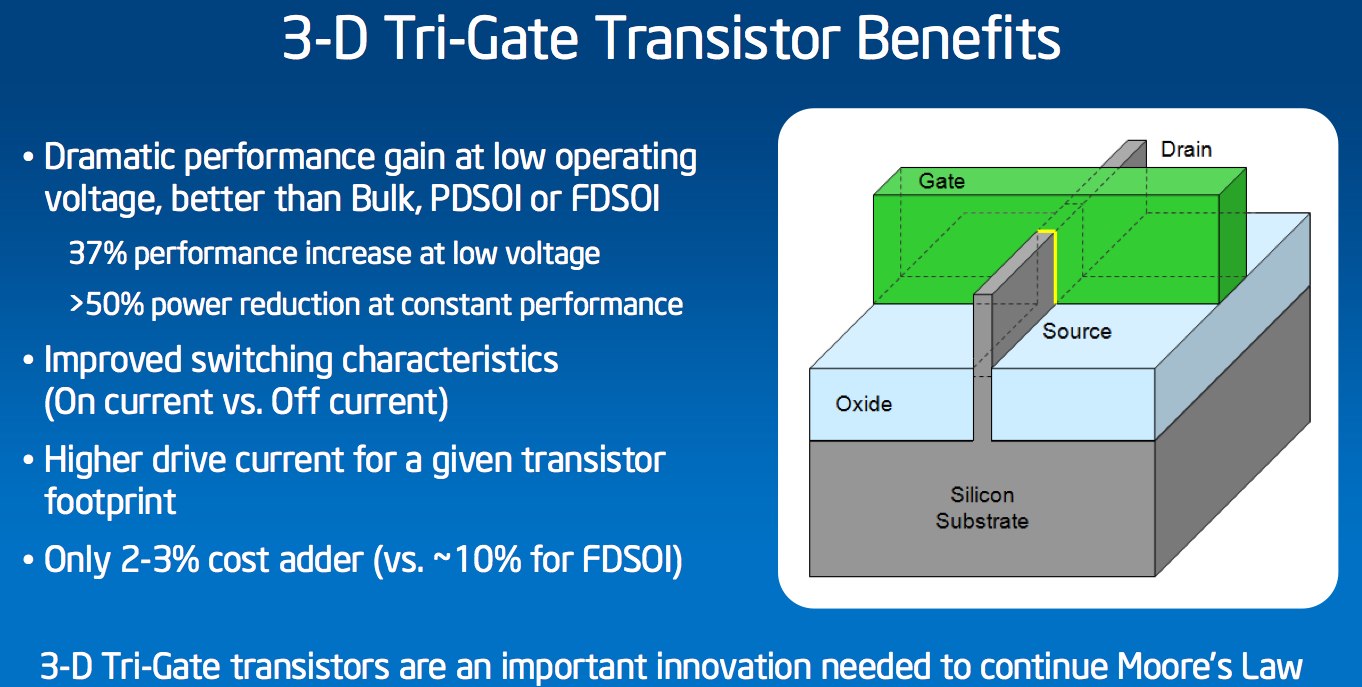
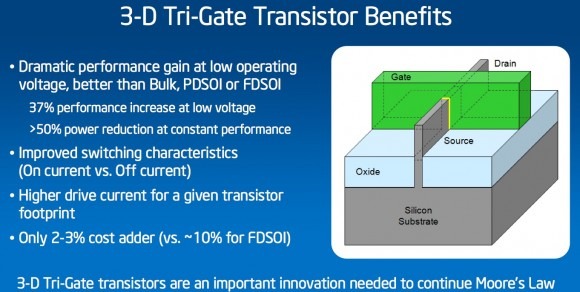
Intel's 3-D Tri-Gate transistors enable chips to operate at lower voltage with lower leakage, providing an unprecedented combination of improved performance and energy efficiency compared to previous state-of-the-art transistors. The capabilities give chip designers the flexibility to choose transistors targeted for low power or high performance, depending on the application.
The 22nm 3-D Tri-Gate transistors provide up to 37 percent performance increase at low voltage versus Intel's 32nm planar transistors. This incredible gain means that they are ideal for use in small handheld devices, which operate using less energy to "switch" back and forth. Alternatively, the new transistors consume less than half the power when at the same performance as 2-D planar transistors on 32nm chips.
"The performance gains and power savings of Intel's unique 3-D Tri-Gate transistors are like nothing we've seen before," said Mark Bohr, Intel Senior Fellow. "This milestone is going further than simply keeping up with Moore's Law. The low-voltage and low-power benefits far exceed what we typically see from one process generation to the next. It will give product designers the flexibility to make current devices smarter and wholly new ones possible. We believe this breakthrough will extend Intel's lead even further over the rest of the semiconductor industry."
Continuing the Pace of Innovation – Moore's Law
Transistors continue to get smaller, cheaper and more energy efficient in accordance with Moore's Law – named for Intel co-founder Gordon Moore. Because of this, Intel has been able to innovate and integrate, adding more features and computing cores to each chip, increasing performance, and decreasing manufacturing cost per transistor.
Sustaining the progress of Moore's Law becomes even more complex with the 22nm generation. Anticipating this, Intel research scientists in 2002 invented what they called a Tri-Gate transistor, named for the three sides of the gate. Today's announcement follows further years of development in Intel's highly coordinated research-development-manufacturing pipeline, and marks the implementation of this work for high-volume manufacturing.
The 3-D Tri-Gate transistors are a reinvention of the transistor. The traditional "flat" two-dimensional planar gate is replaced with an incredibly thin three-dimensional silicon fin that rises up vertically from the silicon substrate. Control of current is accomplished by implementing a gate on each of the three sides of the fin – two on each side and one across the top — rather than just one on top, as is the case with the 2-D planar transistor. The additional control enables as much transistor current flowing as possible when the transistor is in the "on" state (for performance), and as close to zero as possible when it is in the "off" state (to minimize power), and enables the transistor to switch very quickly between the two states (again, for performance).
Just as skyscrapers let urban planners optimize available space by building upward, Intel's 3-D Tri-Gate transistor structure provides a way to manage density. Since these fins are vertical in nature, transistors can be packed closer together, a critical component to the technological and economic benefits of Moore's Law. For future generations, designers also have the ability to continue growing the height of the fins to get even more performance and energy-efficiency gains.
"For years we have seen limits to how small transistors can get," said Moore. "This change in the basic structure is a truly revolutionary approach, and one that should allow Moore's Law, and the historic pace of innovation, to continue."
World's First Demonstration of 22nm 3-D Tri-Gate Transistors
The 3-D Tri-Gate transistor will be implemented in the company's upcoming manufacturing process, called the 22nm node, in reference to the size of individual transistor features. More than 6 million 22nm Tri-Gate transistors could fit in the period at the end of this sentence.
Today, Intel demonstrated the world's first 22nm microprocessor, codenamed "Ivy Bridge," working in a laptop, server and desktop computer. Ivy Bridge-based Intel® Core™ family processors will be the first high-volume chips to use 3-D Tri-Gate transistors. Ivy Bridge is slated for high-volume production readiness by the end of this year.
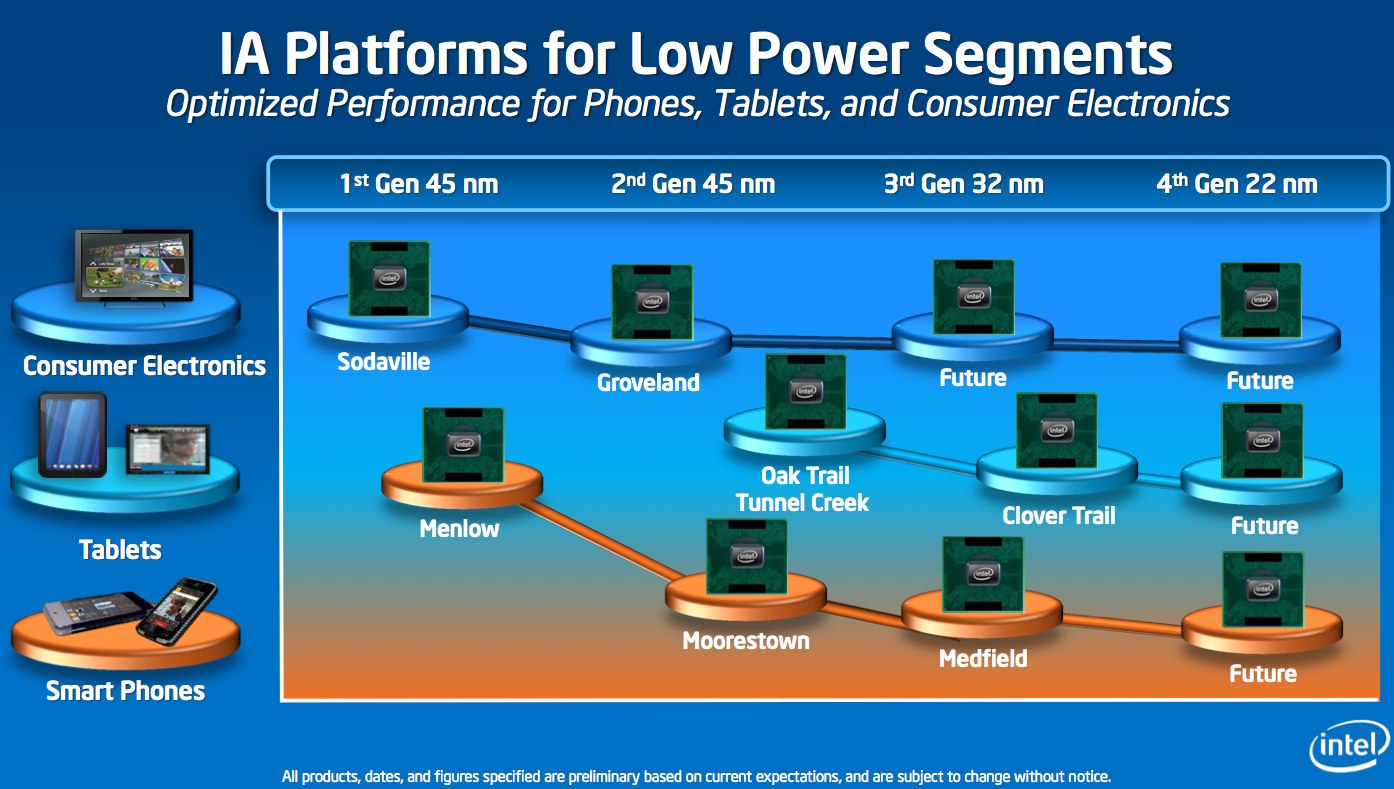
This silicon technology breakthrough will also aid in the delivery of more highly integrated Intel® Atom™ processor-based products that scale the performance, functionality and software compatibility of Intel® architecture while meeting the overall power, cost and size requirements for a range of market segment needs.