What Is The Honda E-Clutch And How Is It Different From A Regular Motorcycle Clutch?
Riding a motorcycle is one of life's most exhilarating thrills, and it comes with a whole culture of clubs and passion. Motorcycles are celebrated for their agility and speed, especially when one rides the fastest V8 motorcycles ever produced. Honda, one of the top motorcycle brands, has been pushing the boundaries of the vehicle's tech, from the world's first motorcycle airbag in 2005, to the Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) in 2010, to the Honda Riding Assist in 2017. And just a few months ago, the brand unveiled another game-changing tech upgrade: an E-Clutch system.
The Honda E-Clutch adds a twist to manual transmission motorcycles. Traditional DCTs automate gear changes and are available on models like the legendary Honda NC750X. On the other hand, the E-Clutch simplifies the clutch operation while preserving the engaging manual shift controls, eliminating the need for constant clutch operation. Unveiled as the world's first electronically controlled clutch system, the E-Clutch is available on the 2024 CB650R and CBR650R motorcycles. It makes gear shifts smoother while reducing the risk of stalling, and it's made for all riders. New riders will appreciate the now-lower learning curve associated with manual versions, and experienced riders love the E-Clutch's adaptability on twisty roads. But how does the E-Clutch work?
What is the Honda E-Clutch system?
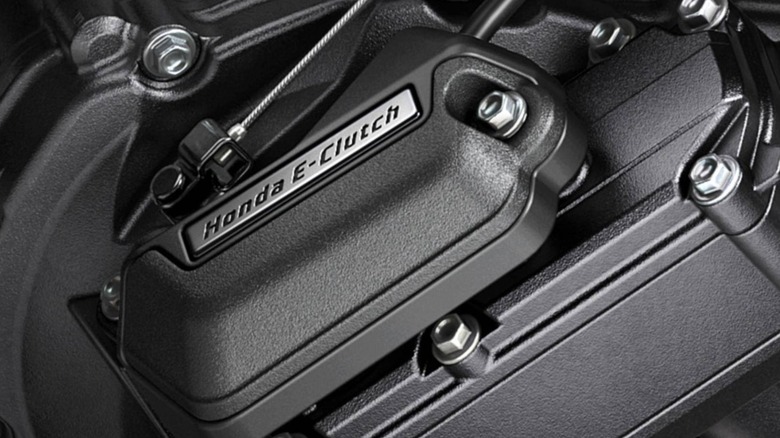
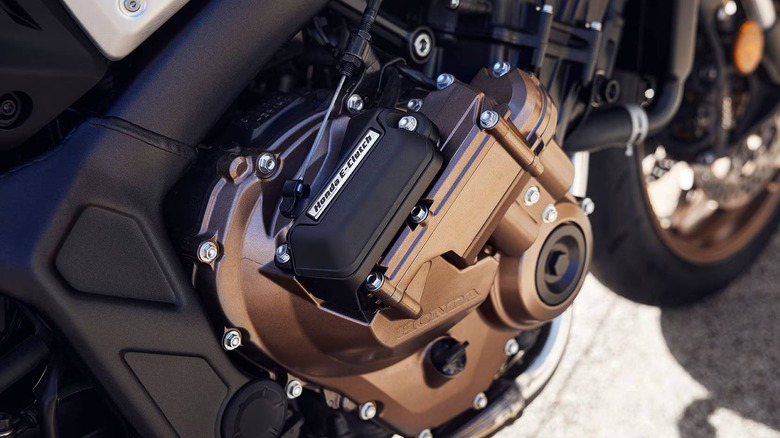
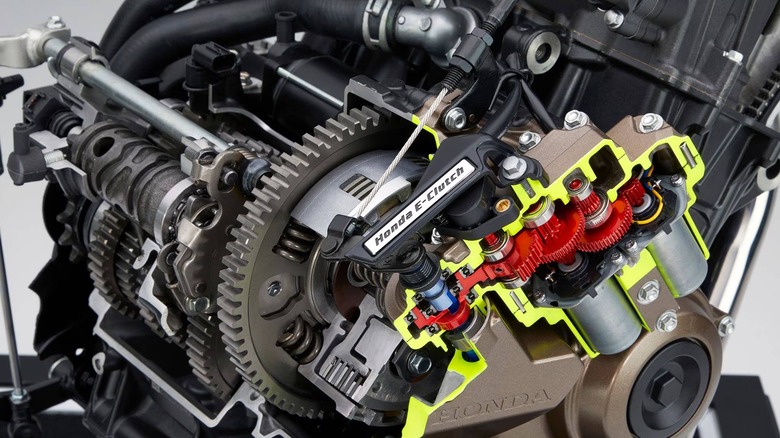
The Honda E-Clutch is an electronically controlled clutch system that automates key functions of a manual clutch on a motorcycle. Unlike the conventional systems, the E-Clutch eliminates the need for manual engagement and disengagement of the clutch lever during starting, shifting gears, and stopping. This advanced system allows riders to enjoy a smoother and more intuitive ride.
According to Honda, the E-Clutch system coordinates engine and clutch controls to optimize performance. It uses sensors to monitor the engine speed, throttle position, shift pedal pressure, and gear selection. Using this real-time data, the system adjusts the clutch operation. This sensor-induced automation is seamless, as is the power transmission between the engine and drivetrain, giving you a smooth drive quality.
What truly sets the E-Clutch system apart is its hybrid functionality. Riders can effortlessly switch between the fully automated clutch control and manual operation by engaging the clutch lever. This flexibility allows riders to navigate through stop-and-go city traffic and tackle twisty roads easily. The E-Clutch system can also be integrated into existing engine layouts without major modifications, thanks to the lightweight and compact design.
What are the key differences between the E-Clutch and a regular clutch?
A regular motorcycle clutch has a basic yet important purpose: to temporarily disconnect the engine from the transmission during shifts. The left lever — which you pull when changing gears — is hydraulically mated to a circular clutch assembly that's positioned near the engine. A manual clutch relies on driver input to disengage the drivetrain, which powers the rear wheel. While its design is effective, it demands precision, which can be challenging for new riders. The E-Clutch, on the other hand, uses a network of sensors and actuators that work in real-time to manage the shifting processes.
One awesome feature of the E-Clutch is its ability to switch between manual and automatic modes, with the automatic as the default. To engage, simply start the bike in neutral, shift into gear, and let the ECU electronically handle the clutch operation. This dual functionality provides riders with the freedom to use the clutch lever manually when desired, a capability absent in traditional clutches. While shifting without a clutch is possible on a manual bike — like when it is in motion — it could damage your transmission.
Another notable difference between the E-Clutch and a regular manual clutch is in safety during emergency stops. You have to pull the manual clutch in when you hit the panic brake to prevent an engine stall. Then when you're in the clear, simply downshift and go. But it's challenging to remember the clutch when you're in an emergency. The E-Clutch, on the other hand, lets you stop in any gear, thanks to its ability to manage power delivery. It will keep running even when you come to a full stop in sixth gear. A warning light prompts the rider to downshift, but the motorcycle remains operational. Riders can even resume motion from a complete stop and get back on the road in the same sixth gear, though the acceleration will be a little sluggish. This makes the E-Clutch a safer and more convenient alternative.
The Honda E-Clutch vs. Dual-Clutch transmission -- differences?
The Honda's E-Clutch shares some similarities with the Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT), yet the two serve different purposes. The DCT works on automating all gear changes, which allows riders to focus on throttle and braking inputs. On the other hand, the E-Clutch semi-automates the shifting process and leaves the gear selection to the driver for manual engagement. This way, the E-Clutch sits between the traditional manual transmission systems and fully automatic transmissions. Nevertheless, there are a lot of Honda motorcycles with the DCT, such as the Honda Goldwing DCT and the NC750X DCT models.
Another key difference between these two components is the weight. The DCT system is heavier, adding around 25 pounds to a bike, whereas the E-Clutch is lighter at just 4.4 pounds (2 kg). Also, the E-Clutch doesn't require a completely re-engineered transmission. The DCT, however, requires a full dual-clutch built into the drivetrain.
All things considered, the DCT might be a better option for riders who need a fully automated experience. The E-Clutch is more of a combination of manual engagement and electronic precision. It opens the door for beginners who want to experience manual riding.