Thunderbolt 4 Vs. USB4: 4 Key Differences And Why They Matter
Thunderbolt 4 and USB4 represent the latest advancements in connectivity technology, offering impressive speeds and versatility for modern devices. With data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps, support for high-definition video, and strong power delivery, both standards are ideal for anyone looking to enhance their workflow — whether in creative, professional, or everyday settings. They also utilize the universally adopted USB-C connector, which provides a level of convenience and ease of use that is difficult to match.
However, despite their many similarities, there are key differences between Thunderbolt 4 and USB4 that affect performance, compatibility, and device support. These differences are particularly important when deciding which standard is best suited for your needs, whether you're working with high-performance peripherals, setting up complex display configurations, or simply seeking a reliable and efficient data transfer solution. In this article, we'll explore the essential differences between Thunderbolt 4 and USB4, and, more importantly, discuss how they can affect your experience. Let's dive in!
Differences in performance and display support
When comparing Thunderbolt 4 and USB4, one of the standout differences lies in performance consistency. Thunderbolt 4 guarantees reliable 40 Gbps speeds across its certified cables, even those up to 2 meters in length. In contrast, USB4 can only maintain 40 Gbps speeds with cables shorter than one meter, with performance dropping to 20 Gbps when using longer or lower-quality cables. This distinction is particularly important for those who need to handle large file transfers, high-resolution video streaming, or other data-intensive tasks.
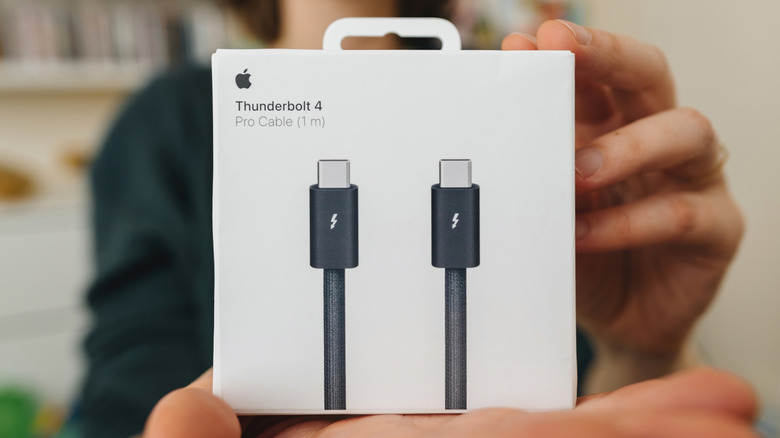
You can easily distinguish Thunderbolt 4 and USB4 cables and ports by looking for the small lightning bolt logo. This logo is found on both the ports and cables. In contrast, USB4 cables display the classic USB logo and are marked with a 20 or 40 designation to indicate their performance capabilities.
Display support is another area where Thunderbolt 4 excels. It allows the connection of either two 4K 60Hz monitors or a single 8K 60Hz monitor. In contrast, USB4 does not support dual-monitor configurations. This difference can be a dealbreaker for professionals such as video editors or graphic designers, who rely on seamless, high-resolution setups for their work. Thunderbolt 4 offers a more reliable and flexible experience in multi-monitor environments.
Differences in speed, power, and device management
The baseline performance guarantees offered by Thunderbolt 4 also surpass those of USB4. While Thunderbolt 4 mandates a minimum link speed of 32 Gbps for devices, USB4 devices can operate with a lower minimum speed of 20 Gbps. Additionally, Thunderbolt 4 requires double the minimum power delivery of USB4, with 15W compared to USB4's 7.5W. This results in faster charging times for devices connected via Thunderbolt 4, making it a more efficient choice for anyone with power-hungry peripherals or workflows that demand rapid charging.
Finally, Thunderbolt 4 supports daisy-chaining of up to six devices, a feature that USB4 lacks. This capability simplifies the management of multiple peripherals with fewer cables, offering greater flexibility for those who have complex workstation setups with devices such as external storage drives, monitors, and other accessories.
All in all, Thunderbolt 4's superior cable certification, guaranteed display support, higher minimum performance standards, and daisy-chaining capabilities make it the clear choice for high-performance and multi-device environments. While USB4 offers flexibility and affordability, its variable performance and feature set may not meet the needs of users who require reliable high-speed connectivity or robust multi-display setups.