How To Speed Up Your Internet Connection On Windows
Having a fast and reliable internet connection is essential for almost everything you do on your Windows PC — from conference calls and streaming your favorite shows to gaming and simply browsing the web. This also means there's nothing more frustrating than dealing with slow internet speeds, especially when you've paid for a high-speed plan. A sluggish internet connection can not only disrupt your daily tasks but also negatively impact productivity, entertainment, and communication.
Such issues can be caused by a variety of factors, including incorrect network settings, interference from nearby devices, and even malware that consumes bandwidth in the background. Fortunately, these problems can often be fixed with a little troubleshooting. From adjusting your network settings and changing DNS servers to eliminating unnecessary background processes, there are several steps you can take to optimize your internet connection and boost the upload and download speeds on a Windows 10 or 11 PC so you can make the most out of your internet connection, whether for work or leisure.
Use a wired connection or switch to 5GHz Wi-Fi band
The internet speed on your Windows device is significantly impacted by the type of connection you use. For example, a wired Ethernet connection generally provides faster and more stable speeds compared to Wi-Fi. This is because Ethernet avoids common Wi-Fi problems such as interference from other devices, signal loss due to distance, and obstacles like walls or furniture that can degrade signal strength. So, if your router is close to your laptop or PC, consider using an Ethernet cable to enjoy seamless connectivity, especially during bandwidth-intensive tasks, and to avoid high ping while gaming.
If a wired connection isn't practical for you, switching to the 5GHz Wi-Fi band can provide a significant speed boost. Most modern routers support dual-band connectivity, offering both 2.4GHz and 5GHz options, and you can choose your band via the Quick Settings menu on your Windows PC. The 5GHz band typically offers faster data rates and is less congested than the 2.4GHz band, which is often shared by household devices and Bluetooth gadgets. This reduced interference results in more reliable and consistent speeds. The only caveat is that the 5GHz band has a shorter range than 2.4GHz, so you may need to stay closer to the router for optimal performance.
Turn off metered connection and change the DNS server
A metered connection is a feature in Windows that helps conserve data usage, which can be particularly useful if you're on a limited data plan or using your phone as a hotspot. However, if data usage isn't a concern, it's best to disable this feature as it can limit your internet speed. To do this, open the Settings app and head to the Network & internet tab. Then, select your connection type — Wi-Fi or Ethernet — and turn off the "Metered connection" toggle.
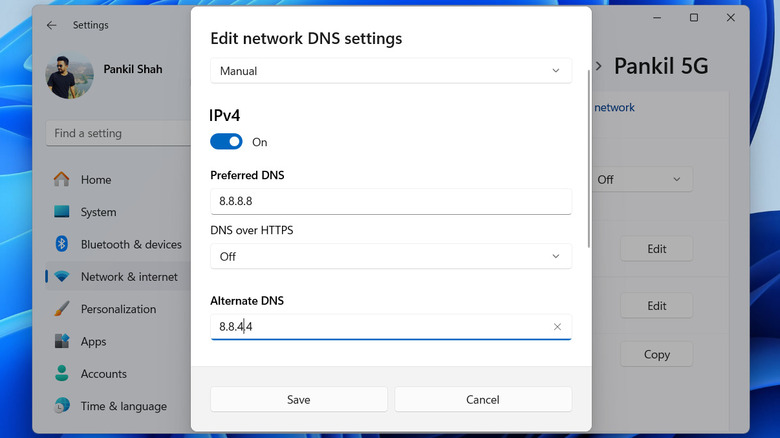
Another effective way to boost your internet performance is by changing the DNS (Domain Name System) server on your PC. The DNS is responsible for translating website names into IP addresses, and if your current DNS server is slow or unreliable, it can cause delays in loading websites. Switching to a faster and more reliable DNS server — such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) — can improve the browsing experience. Here's how to change your DNS server on Windows:
- Press Windows + I to open the Settings app.
- Switch to the Network & internet tab and click the Properties option in the right pane.
- Click the Edit button next to "DNS server assignment."
- Click the drop-down menu to select Manual.
- Enable the IPv4 toggle.
- Type the primary and secondary DNS server addresses in the Preferred DNS and Alternate DNS fields, respectively.
- Click the Save button to apply the changes.
Control internet usage by background apps
Having too many apps running in the background can noticeably impact your internet speed, especially if they consume bandwidth for tasks like syncing data, downloading updates, or uploading files. One way to identify such apps is to check the data usage on Windows. Here's how to do that.
- Press Windows + I to open the Settings app.
- Switch to the Network & internet tab and click on "Advanced network settings."
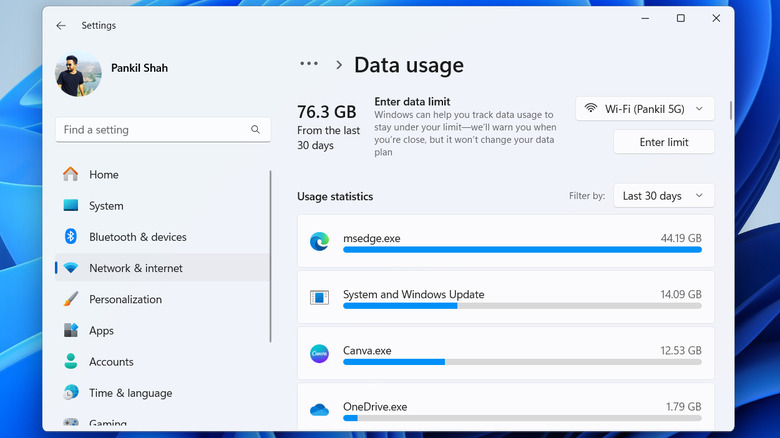
- Under More settings, click on Data usage.
In this menu, you'll see a list of apps and programs along with their data usage. You can use the filter drop-down menu in the top right corner to view data usage for the last 7 days or 24 hours. Once you've identified the apps that are using bandwidth unnecessarily, you can close them manually. You can also prevent those apps from running in the background, so you don't have to worry about using the internet.
For apps like Microsoft Store, you can disable automatic updates by navigating to its settings menu. For OneDrive, you can limit its bandwidth usage by adjusting its settings. Further, you can turn off automatic Windows updates on your PC to prevent them from consuming bandwidth when you're not expecting it. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your internet connection is focused on the tasks you're actively engaged in, such as browsing, streaming, or gaming.
Disable browser extensions and clear browsing data
Using browser extensions — whether for productivity, privacy, or customization — can greatly enhance your browsing experience. However, poorly designed extensions can negatively impact your browser's performance, potentially slowing down your internet speed.
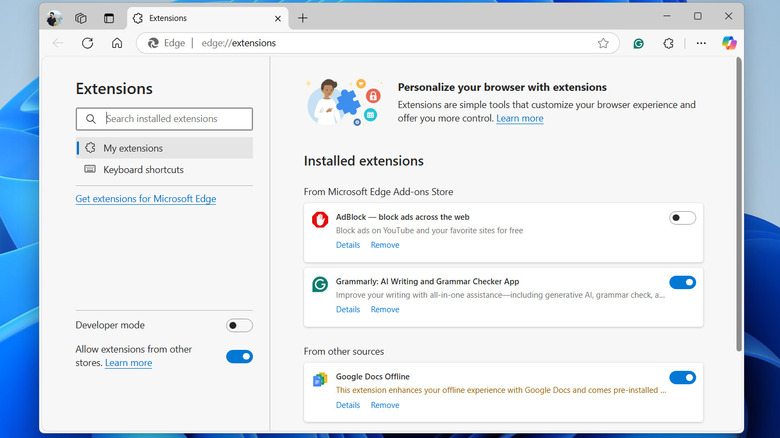
To determine if your extensions are causing slowdowns, try using your browser in incognito or private browsing mode where it runs without any extensions. If you notice a significant speed improvement, it's likely that one or more extensions are causing the issue. To address this, consider disabling or removing problematic extensions. In browsers like Chrome, Edge, or Firefox, you can manage your extensions by clicking the three-dot menu icon and selecting Extensions from the list. From there, you can disable or remove any extensions you no longer need.
In addition to managing extensions, you should also clear your browser's cache and cookies. Over time, cached files and stored data can accumulate and bog down your browser, causing websites to load slowly. To clear your browser cache and cookies in Chrome or Edge, press the Ctrl + Shift + Delete keyboard shortcut to open the "Clear browsing data" panel. In the panel, choose "All time" from the drop-down menu. Then, check the boxes next to "Cookies and other site data" and "Cached images and files." Finally, click the Clear data button to remove the unnecessary files. Similarly, you can clear cache and cookies in any other browser you may be using.
Check for spyware and viruses
Spyware and other malicious software can also severely impact your internet connection on Windows. These harmful programs may secretly consume bandwidth, interfere with browser processes, or run background tasks that drain system resources, all of which can lead to slower performance. If your PC is infected with multiple threats, the impact on your internet speed can worsen. Common signs of spyware infection include random websites opening on their own, slow or erratic system performance, and unusual behaviors like the keyboard typing by itself.
Viruses, similarly, can wreak havoc on your Windows PC and further slow down your internet speed. These viruses can infiltrate your system, corrupt important files, and use up network resources, making your connection sluggish. Often, these threats operate silently in the background, sending and receiving data that consumes bandwidth and slows down both downloads and uploads. To protect your system, it's essential to install reliable antivirus software like Norton 360, Bitdefender, or Malwarebytes. Additionally, the built-in Windows Security app offers a solid first line of defense by automatically scanning for threats and keeping your system secure.
Applying the above steps should help improve internet speeds on your Windows 10 or 11 PC. However, if you continue to experience issues across all your devices, it may be best to contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for assistance. They can diagnose any problems on their end, such as network outages or plan limitations, and provide solutions.