What Is The Difference Between Diesel And Turbo Diesel Engines?
Diesel engines have long been celebrated for their efficiency and durability. They're a mainstay for any enthusiast seeking a robust performance, powering everything from passenger vehicles to heavy machinery. However, there are some things you might not know about diesel engines — like how their performance capabilities and efficiencies hinge on aspects that often go unnoticed by some vehicle owners, such as the inclusion of a turbocharger.
From the launch of the first turbocharger in 1905 to the first commercially produced turbocharged Oldsmobile Jetfire V8 in 1962, turbocharging technology changed how engines perform on the highway and in the field. This technology uses exhaust energy and has benefits that range from increased power to improved fuel consumption. But even without turbochargers, naturally aspirated diesel engines still deliver good pulling power, making them great for hauling or towing. Today, many vehicles offer naturally aspirated and turbocharged diesel engines. But what truly sets these two apart? And do the differences matter to everyday drivers?
What are naturally aspirated diesel engines?
Unlike gasoline engines, which rely on spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture, diesel engines use compression ignition. This process involves compressing the air inside the cylinder to a very high temperature, which generates heat to ignite injected fuel.
The high compression ratios in diesel engines allow them to achieve greater thermal efficiency. This means they can extract more energy from the same amount of fuel compared to gasoline engines. The compression is what makes diesel engines particularly popular in scenarios where fuel economy and torque are critical, such as in trucks, buses, and industrial machinery.
Diesel engines have simpler designs with fewer components. They function without the use of a spark plug, which reduces maintenance needs. However, they often operate at lower RPMs, which gives them more torque. They're also heavy due to reinforced components that help withstand high compression ratios.
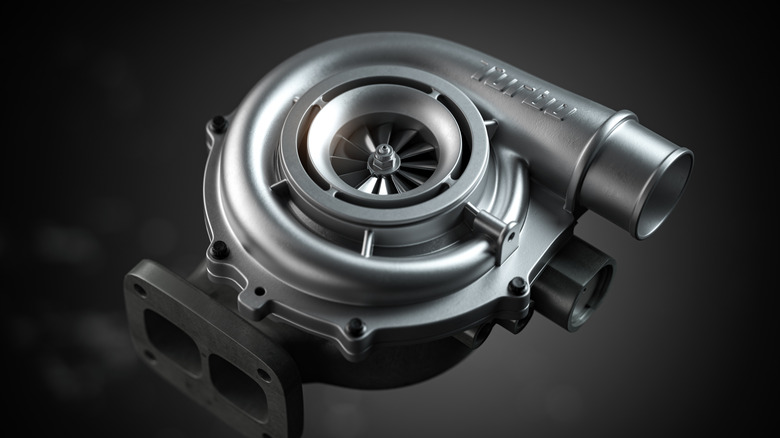
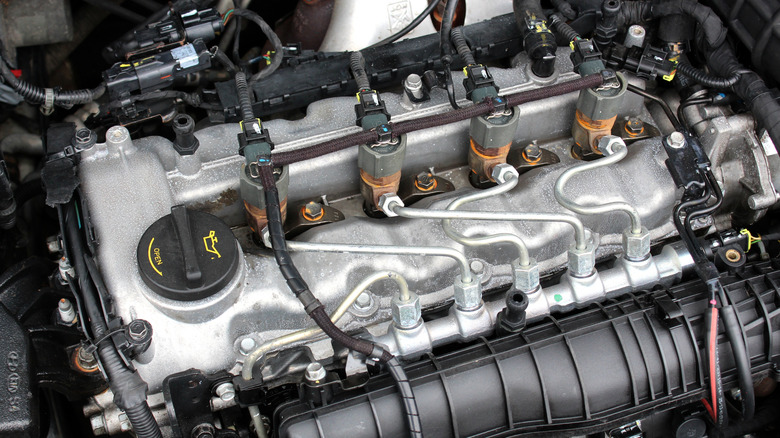
What are turbodiesel engines?
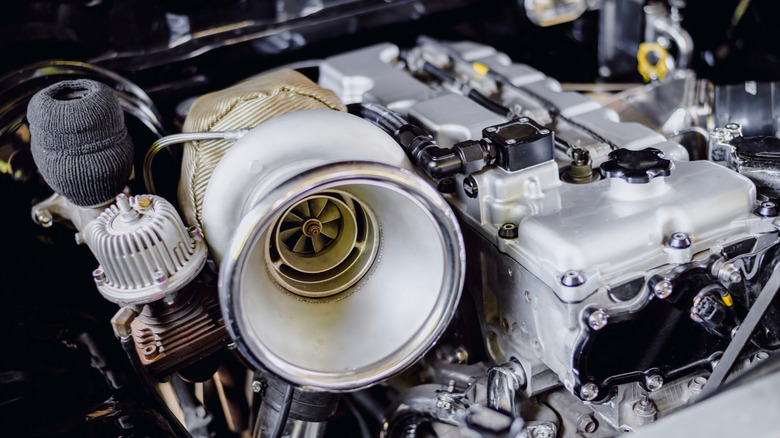
Turbodiesel engines take the same principles as naturally aspirated diesel engines and amplify them with turbocharging technology, which enhances power and efficiency without increasing engine size. A turbocharger uses energy from exhaust gases to drive the turbine. This turbine spins a compressor, which forces more air into the combustion chamber. This increased airflow allows for more fuel to burn efficiently, resulting in a greater power output. For diesel engines, the turbocharger complements the high compression ratios, which gives you low-end torque.
Turbodiesel engines have a strong towing performance. One of the best turbodiesel engines that delivers a good towing capacity is the 420-hp 6.7L Cummins, which gives the Ram 2500 a tow rating of nearly 20,000 pounds when properly equipped. Another option is the Ford 6.7L Powerstroke offered in the Ford F-250, F-350, and F-450 models. Aside from boosted torque, turbodiesel engines produce fewer emissions per mile compared to gasoline engines.
Key differences between diesel and turbo diesel engines
The distinction between diesel and turbodiesel engines lies primarily in their design, performance, and efficiency. Standard diesel engines rely on natural air intake, which limits power output. So, to produce more power, these engines often require a higher displacement. On the other hand, turbodiesel engines can produce more power without increasing size, thanks to the turbocharger. It forces more air into the combustion chamber, which boosts power by enabling fuel to burn more efficiently.
While diesel engines are generally known to be efficient, naturally aspirated versions may not optimize fuel usage because they don't utilize exhaust energy. Turbochargers improve fuel efficiency by reusing the exhaust energy. This allows them to deliver more miles per gallon compared to their non-turbo counterparts. Also, while standard diesel engines provide a steady torque, they lack the dynamic acceleration, which is often required in high-performance scenarios. However, the turbodiesel versions can produce higher torque at lower RPMs, making them perfect for towing.
Efficiency and environmental impact
Due to their ability to re-use the wasted energy in exhaust gases, turbodiesel engines offer better fuel economy. However, with efficiency comes the challenge of complying with emission regulations. One of the reasons why turbochargers have been widely adopted by manufacturers is because they make engines smaller and more efficient. Automakers like BMW and Mercedes-Benz have transitioned to turbochargers across their lineups, leaving the non-turbo naturally aspirated options behind.
Because they operate at increased temperatures, diesel engines emit higher levels of Nitrogen Oxide (NOx). Turbochargers allow manufacturers to use smaller engines that comply with these emissions laws. As a result, there aren't many naturally aspirated diesel engines left these days.
The push for cleaner emissions has had some challenges. One of the infamous events in diesel history is the Volkswagen emissions scandal, also known as "Dieselgate." In 2015, the brand was caught using "defeat devices" that manipulated NOx emissions during tests, only to emit 40 times the legal limit when on the road. The fallout reshaped the industry, driving changes in power, efficiency, and, at the center of it all, the turbocharger.