How To Fix The No Internet, Secured Error On Windows
Windows users face many different issues on their system, and one such common Windows error is the "No Internet, Secured," which occurs while connecting to a network. This network error indicates that your computer is connected to a Wi-Fi or Ethernet network, but the internet is inaccessible. This is a confusing situation because connections appear to be secure, yet there's no internet.
It can be really frustrating to face this issue when you heavily rely on a stable internet connection for your work, communication, and entertainment. There are various reasons it can occur. The network settings on your system might be incorrectly configured. You are successfully connected to the network, but the internet plan might be inactive. The outdated Windows and the network adapters are another cause of such internet issues.
If you repeatedly encounter this issue and are unable to solve it, this guide will provide you with various working solutions and step-by-step instructions for applying them. The steps in this guide are performed on a Windows 11 device, but all of them are applicable on Windows 10, too, with slightly different names for certain settings.
Preliminary checks to fix No Internet, Secured error
Before making any serious amendments to Windows settings, make some basic checks to fix some minor or temporary issues that might be causing this error. If you are connected to a hotspot network of your mobile device, ensure that the internet connection on your phone is turned on and that you have an active internet plan. If you are connected to a router and are sure that your internet plan is active, restart the router and modem to eliminate any temporary glitches.
Modern routers support dual-band—2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Your device might be incompatible or having trouble connecting to your current network frequency. Try changing from 5 GHz to 2.4 GHz or vice versa, and check if the internet is working. Next, connect other devices to the same network and check if the internet is working on those. If yes, then the problem is device-specific. If you haven't updated your Windows for a long time, it might be causing compatibility issues, leading to such internet errors. Regularly update your Windows to avoid common problems. If you have turned on a VPN and the issue started just after that, it is advised to turn it off to restore the connection. Lastly, contact your internet service provider and check if there is any issue on their side or an outage around your area.
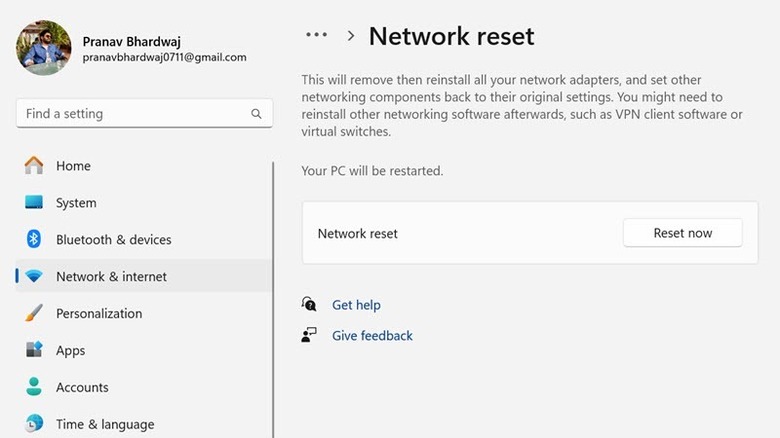
Perform network reset
If you recently updated your Windows or Network Adapters, this new action might have caused a glitch in the network settings, causing the "No Internet, Secured" error. To counter this, you need to reset your network settings. This will set your system's networking components back to their original state. Remember that your system will be restarted after the network reset is complete, so save all your unsaved work before hitting the reset button. Here's how to perform a network reset on Windows 11:
- Click the Start button and select Settings from the Start Menu.
- Switch to the Network & Internet section on the left pane, and on the right, scroll down and click the Advanced Network Settings.
- Look for the Network Reset option and select it.
- Finally, click the Reset now button. On the prompt, confirm the action by clicking the Yes button.
Also, remember to take note of the passwords of all the saved networks of your system. You will also need to re-install VPN clients and virtual switches. After the above action, your Windows will be signed out within 5 minutes and then restart with factory reset network settings. Connect to the network that was causing the error and check if it's fixed.
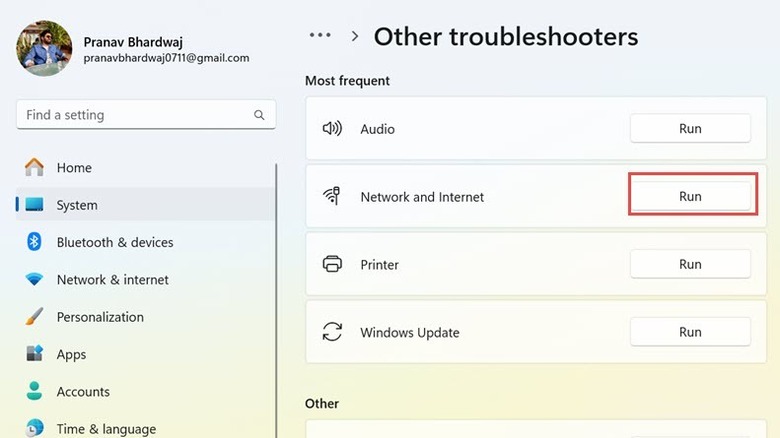
Run network and internet troubleshooter
Windows OS is prone to troubles, so Microsoft has included an in-built troubleshooter section with various dedicated troubleshooters to diagnose and solve common Windows issues. One of those is the Network and Internet troubleshooter to solve internet-related problems. To run this troubleshooter on Windows 11, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows + I keys to launch Settings.
- Switch to the System tab on the left pane and select the Troubleshoot option on the right.
- Next, select the Other Troubleshooters option.
- Finally, click the Run button next to the Network and Internet troubleshooter option.
- Follow the onscreen instructions and let the troubleshooter diagnose the problem.
Apply the solutions suggested by the troubleshooter to fix your system's internet-related issues. After making changes to the recommended settings, restart your system. Running it might reveal the root cause of the issue you are facing, which may have eluded you before.
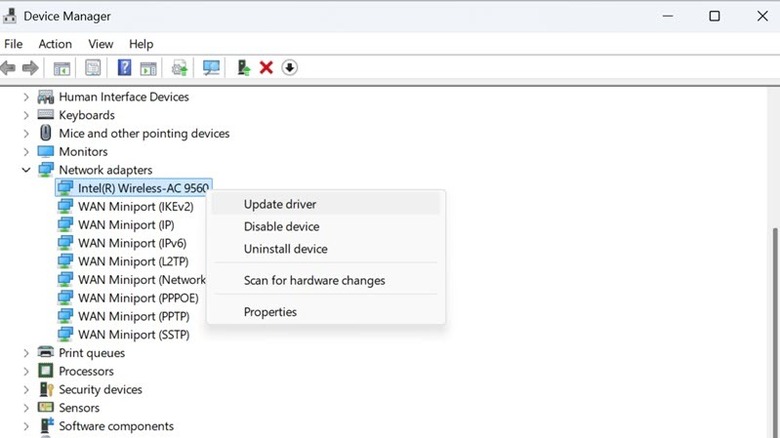
Update and re-install network adapter driver
Outdated or corrupted network adapters are the primary cause of internet-related issues, including the "No Internet, Secured" error. You can download the latest drivers from the manufacturer's website or let Windows search for them automatically. To update Network Adapters, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Device Manager from the menu.
- Look for the Network Adapters section and expand it.
- Right-click on your network adapter, which shows the error, and select the Update Driver option.
- If you don't have the latest drivers on your computer, click the Search Automatically for Drivers option. If you have manually downloaded the drivers from the manufacturer's website, select the Browse My Computer for Drivers option and browse for the downloaded drivers.
- Follow the onscreen instructions to successfully update the drivers.
After successfully updating the drivers, restart your system to make the changes effective. If the error persists, try uninstalling and then re-installing the network adapter. To do that, expand the Network Adapters section,right-click on your network adapter, select the Uninstall Device option, and restart your computer. After the restart, Windows will automatically attempt to re-install the latest network adapter driver. To check if the driver is installed, launch the Device Manager and look for it under the Network Adapters section.
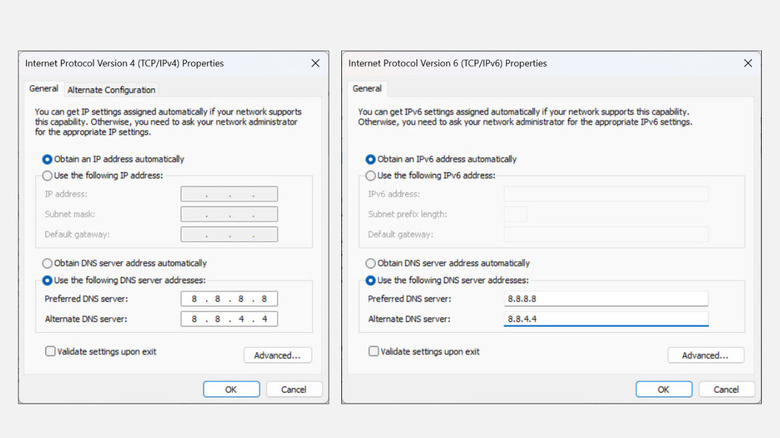
Change DNS server and clear DNS cache
Incompatible DNS settings can result in no internet connection, even if you are connected to the network safely. To counter this, you can change to some popular and reliable DNS servers such as Google DNS, OpenDNS, and Cloudflare instead of using the default server of your ISP. Check if the problem is solved after this step. Next, you can try flushing the DNS caches. To flush DNS caches on Windows, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows + X keys on your keyboard to launch the Power Menu.
- Select Terminal (Admin) or Command Prompt (Admin) from the list.
- Type this command and hit the enter key to flush DNS caches: ipconfig /flushdns.
You will see a success message. Exit the command line window and check if the issue is solved. DNS caches help the website load faster, but if you are facing connectivity issues, it is best to flush them and start fresh.
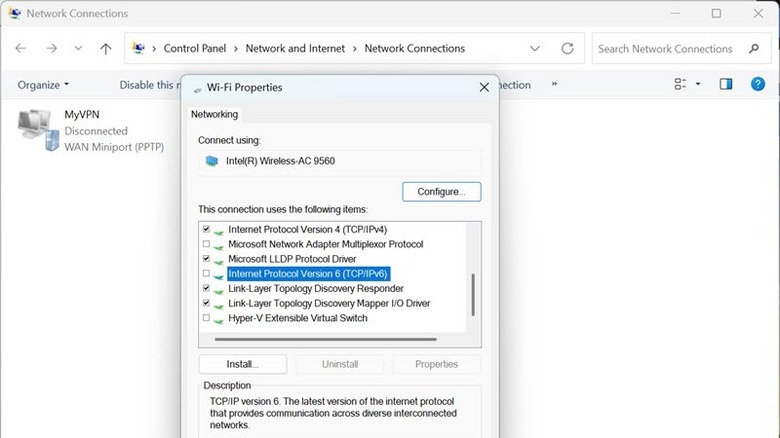
Temporarily disable IPv6
The Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest internet protocol to manage the traffic across the internet. If the error persists, try disabling the IPv6 temporarily. It is generally not recommended to do so, but it might fix the internet-related issue you are facing. Here's how to do that:
- Type Control Panel on the Windows search box, and click its icon to launch it.
- Under the Network and Internet section, click the View Network Status and Tasks.
- On the left side, click the Change Adapter Settings.
- Right-click on your problematic network and select Properties.
- Under the Networking tab, look for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and uncheck it.
- Click OK and close the Properties window.
Check if performing the above action resolved the "No Internet, Secured" error. If it still isn't solved, contact your ISP and ask them to help you troubleshoot the issue. It might be possible that there's a wiring problem or that the router itself is damaged. Your ISP should find out and resolve any such problems.