Here's What Each Of The Sensors In Your Smartphone Actually Do
It turns out that the name "smartphone" is pretty accurate, as we hold an incredibly complex piece of technology in our pockets. From the camera to the screen and everything in between, industry titans like Apple, Samsung, and Google continue to improve the tech inside your phone, and the sensors may be the most impressive part.
Now, we all know there are plenty of sensors inside your smartphone, and we'd probably be here all day listing every single one. Thankfully, most can be sorted into three major categories: motion, location, and environmental sensors. Motion sensors are more or less the top dogs of smartphone sensors, measuring things like acceleration and gravity. Location sensors practically speak for themselves, allowing your smartphone to track your physical location. Environmental sensors measure natural data, like humidity, pressure, and temperature, which are essential for features like the weather and stopping your phone from overheating.
When used together, the three different sensors bring your smartphone to life, turning the pocket-sized tech into a vital tool for everyday life. However, those categories are broad, so let's break down some of the more important sensors found in every smartphone and what they actually do.
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is the first piece of complex sensor technology in your smartphone, and — surprise — it measures acceleration. Of course, it's much more complicated than that, as there isn't just one large motion sensor in your phone but many smaller sensors working together to calculate data like gravity, vibrations, and tilt. With that information, your phone can tell how fast it's moving and which direction it's going.
Many apps have features that put your smartphone's accelerometer to work. Any health and fitness apps — like Apple Health, Google Fit, and Samsung Health — that track your daily steps in real time can do so because of the accelerometer. Apple Maps and Google Maps use it to track how fast you're moving. It's how they can estimate your arrival time or use it in tandem with local information to compare your current speed to the speed limit. Even Snapchat uses your phone's accelerometer in its interactive map, putting a cute car around your bitmoji when it registers you're moving in a vehicle.
Gyroscope
Have you ever wondered how your smartphone knows which orientation it's in? Your camera automatically switching between portrait and landscape mode is incredibly convenient, but it wouldn't be possible without the gyroscope.
Gyroscopes work alongside the accelerometer to measure your smartphone's angular velocity, tracking any changes in the device's rotation while always knowing which direction is up. It knows when you turn your phone sideways, adjusting the on-screen image to the device's new orientation. It's why iPhones and Androids have auto-rotate and orientation-locking features to control when you can and can't rotate your screen. While this article focuses on its uses in smartphones, gyroscopes are prominent in many technologies, including airplanes and gaming consoles.
Any app that utilizes your phone's movement uses its gyroscope. Think back to when Doodle Jump dominated the mobile games industry, forcing everyone to tilt their phone to make sure the character kept jumping up. Similarly, any racing game where you tilt your phone like a real-life steering wheel has the gyroscope to thank. While games often make use of gyroscopes, iPhone cameras also put the tech to work with panoramic pictures and slow-motion videos. And, like the accelerometer, gyroscopes help your device's GPS, ensuring you never get lost.
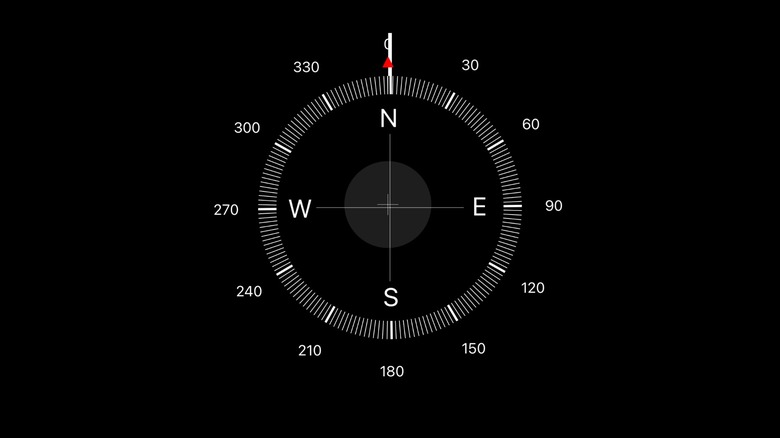
Magnetometer
If you haven't put it together by now, many smartphone sensors work together to figure out the device's physical location, and the magnetometer is just another cog in the wheel. Like other smartphone sensors, you can likely guess what the magnetometer does from its name — it helps your device figure out its orientation in space, determining your location relative to the Earth's magnetic poles. In simpler terms, your phone's magnetometer measures the surrounding magnetic fields and can then tell you which direction is north.
Naturally, you can thank your phone's magnetometer for giving your compass app life. Whenever you open the application, the sensors immediately kick in, bringing the usefulness of a compass to the convenience of your hand. Like the other sensors mentioned in this list, magnetometers (and compasses) play a vital role in bringing your smartphone's GPS to life. Without them, your phone wouldn't know which direction was north.
GPS
As one of the most used sensors in your smartphone, it's no surprise that the GPS found its way onto this list. Every smartphone comes installed with Global Positioning System technology, which works with the other sensors included in this list.
GPS units inside your smartphone work by sending signals up to free-use government satellites orbiting the Earth, which then transmit the signal back to your device. Then, the GPS receivers in your phone calculate how long it took the signals to return from the satellites, triangulating your position on the planet. So, when you allow your smartphone's operating system to share your location with a GPS app, your phone can track you in real time. And since GPS primarily works off satellites, your navigation continues even when you don't have service. Because of that, many great offline GPS apps exist for iPhones and Androids. However, factors like cell signal strength and other data can improve your device's GPS tracking.
Naturally, apps like Apple Maps, Waze, and Google Maps put your smartphone's GPS units to work. All rideshare apps (Uber, Lyft, etc.) also utilize GPS tech, while social media apps like Snapchat and Instagram boast GPS features that can pinpoint your current location.