4 Apple Watch Safety Features That You Should Know
The Apple Watch is one of Apple's most underrated products. While it's certainly an aesthetically appealing device, it offers much more than just features that help you stay in shape. Thanks to the powerful sensors the Apple Watch is equipped with, the wearable device packs in multiple safety features like crash detection, fall detection, and medical ID, among others.
Although Apple has designed the Apple Watch to be extremely easy to navigate, a few of these features — like the ECG app — are buried deep within the settings and extremely easy to miss. You may have bought your Apple Watch a few months ago but have yet to realize how powerful it really is. These could very well be the features that save your life or that of someone you love someday. So, whether you're a senior citizen or a high school student, it's a good idea to familiarize yourself with the following Apple Watch safety features beforehand.
ECG App
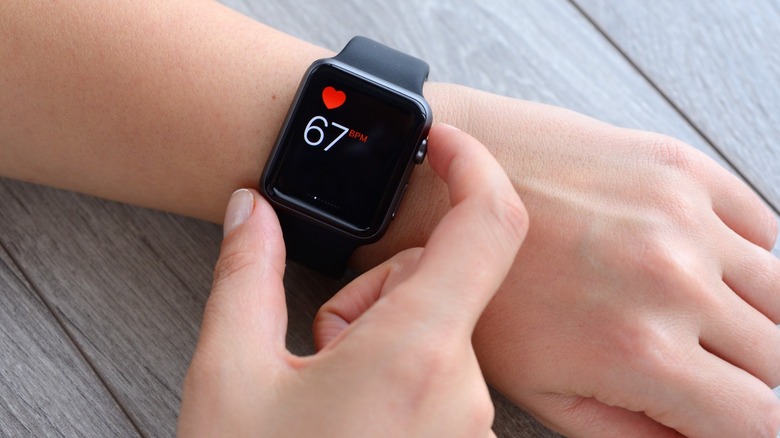
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records electrical signals in the heart. While it's generally a painless test done in clinics or hospital rooms, your Apple Watch is also capable of taking an ECG and potentially saving your life. The ECG app is available on the Apple Watch Series 4 and subsequent models, leveraging the device's electrical health sensor.
Before taking an ECG, you must install the ECG app on your Apple Watch. You can do this either via your device's App Store or by opening the Watch app on your iPhone and going to Heart. After that, go to the ECG section and tap Install. Once it's downloaded, launch the app to take an ECG.
If you haven't set up the ECG app yet, open the Health app on your iPhone and choose the Browse tab at the bottom of the screen. Go to Heart and then Electrocardiograms and tap Set Up. Once you're all set, launch the ECG app on your Apple Watch and hold a finger from your free hand on the digital crown for 30 seconds. Make sure not to press or move your finger when the reading is in progress, as the slightest interruption can make the ECG restart.
When you're taking an ECG, make sure to rest your arms on an even and steady surface, like a table. After the ECG reading is successfully taken, you should see one of the following results on your Apple Watch's screen: sinus rhythm, martial fibrillation, low or high heart rate, inconclusive, or poor recording.
Crash Detection
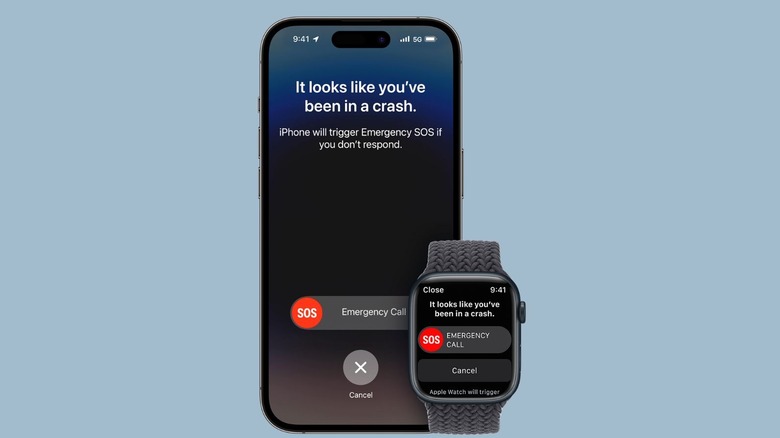
Like the iPhone 14 and above, the Apple Watch Series 8, Series 9, and SE (2nd Generation) are equipped with a feature called crash detection. This feature leverages the watch's three-axis gyroscope and accelerometer to detect sudden changes in g-force, which are usually indicative of a severe car crash. Apple executives explained to TechCrunch in 2022 that the watch can detect up to 256 Gs.
Along with the gyroscope and accelerometer, the device uses a combination of GPS speed readings, loud noise detection from the microphone, and even barometric pressure changes, which are often caused by the deployment of airbags. While these won't trigger crash detection independently, a combination of multiple indicators in tandem will set off the feature.
When the Apple Watch detects a severe car crash, an alarm will sound and a screen will immediately pop up, asking if you'd like to call emergency services. You then have 20 seconds to close the pop-up if it's a false alarm, after which the watch will send the alert. The call sent out includes a repeating message, as well as your physical coordinates.
Wrist Temperature
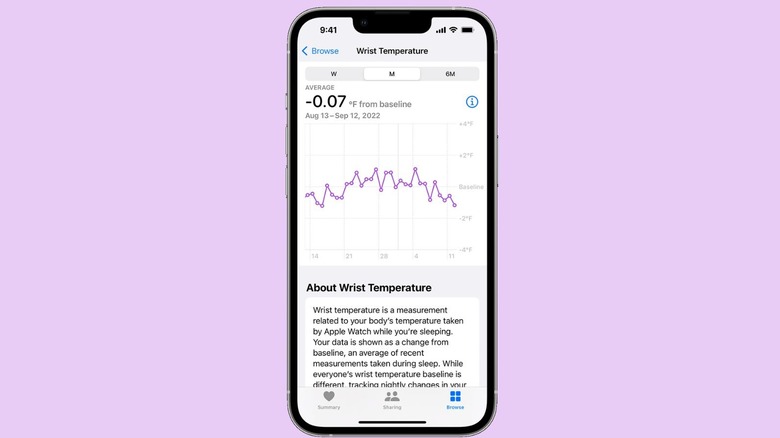
The Apple Watch Ultra, Series 8, and Series 9 include a feature called Wrist Temperature Tracking, which essentially lets a user know how warm or cold they get when they're sleeping. This feature uses two different temperature monitoring sensors and samples your temperature every five seconds during sleep.
After five nights of tracking your wrist temperature, your watch will establish a baseline wrist temperature based on the data gathered. It's important to know, though, that while Wrist Temperature Tracking can gather helpful data to help give you some insight into your overall physical well-being, Apple stresses that it's not intended for medical use and cannot measure your temperature on demand like a thermometer.
To use Wrist Temperature Tracking, you need to have Sleep set up and Track Sleep with Apple Watch toggled on. You also need to have Sleep Focus enabled for at least four hours a night. You can view your wrist temperature data by heading to the Health app and going to Browse, Body Measurements, and then Wrist Temperature.
Emergency SOS
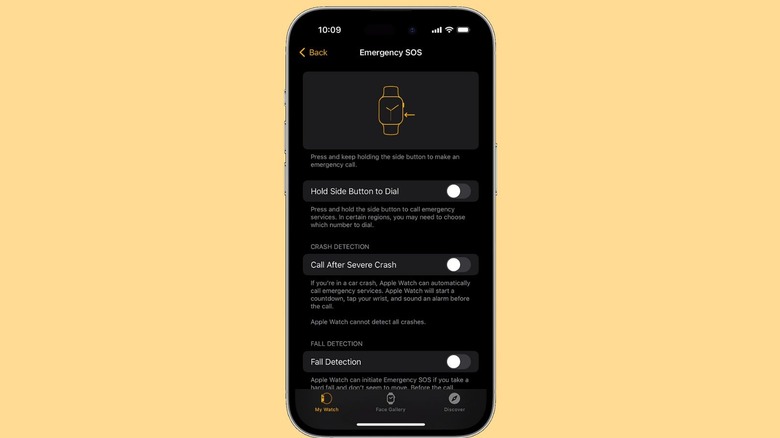
If you ever find yourself stuck in a dangerous situation and are unable to physically dial the number for emergency services, you can use the Emergency SOS feature on your Apple Watch. Similar to the Emergency SOS feature on iPhones, all you need to do to trigger this feature is press and hold the Apple Watch's side button under the crown. Keep doing so until you see the following three sliders: Medical ID, Compass Backtrack, and Emergency Call. You can either drag the Emergency Call slider or continue holding your side button, which will trigger a countdown to call local emergency services.
If you'd like to notify your loved ones when you're stuck in a dangerous situation, make sure you save them as emergency contacts by heading to the Health app on your iPhone and tapping your profile icon in the upper-right corner of the screen. Tap Medical ID then Add Emergency Contacts and simply select your loved ones from your contact list.
Once this is set up, Emergency SOS will both notify emergency services and text your own emergency contacts with your current location. For the feature to work properly, you must have either cellular connectivity or an Internet connection to use Wi-Fi calling. While we hope that this is a feature you'll never have to use, it's certainly good to know that it's there if you find yourself stuck in a life-threatening situation.