Why Is Your Ethernet Slower Than WiFi (And What You Can Do To Fix It)?
Compared to the early days of wireless internet, Wi-Fi signals are much more reliable in terms of stability and speed. That said, the efficacy of Wi-Fi is still subject to a variety of external factors. This can include the distance and obstacles between your computer and your router, your router's signal strength, and your computer's wireless adapter. As any regular LAN party attendee can tell you, when the Wi-Fi isn't working properly, it's time to hook up a hard line.
Nine times out of 10, plugging your computer directly into your internet router via an ethernet cable will immediately get you a faster, steadier internet connection. Data flows cleaner through a cord than it does through the air, after all. That said, even an ethernet cord isn't an absolute fix. A handful of quirks could hamper your connection and make Wi-Fi seem faster by comparison. Instead of living in this bizarre, backward universe, you need to diagnose and fix the problem.
How to diagnose the problem
Using an ethernet cable for your internet is a much less abstract proposition than connecting with Wi-Fi since it's a hard cable that you can pick up and move around. As such, if you're having problems with your ethernet Wi-Fi, the problem is most likely of a physical nature, either with the cable itself or with the ports you're trying to plug it into. If you live with pets or have a pest problem, it's possible that either the cable or ports have sustained physical damage, though it's also possible that you're just using the wrong cord.
While physical problems are more likely, though, you shouldn't write off software problems entirely. If you're getting a steadier connection from Wi-Fi than ethernet, your computer's network settings may be configured in a weird way that's preventing the cord from properly transferring data. This can be remedied with a bit of tinkering in your computer's settings and drivers.
How to fix hardware ethernet problems
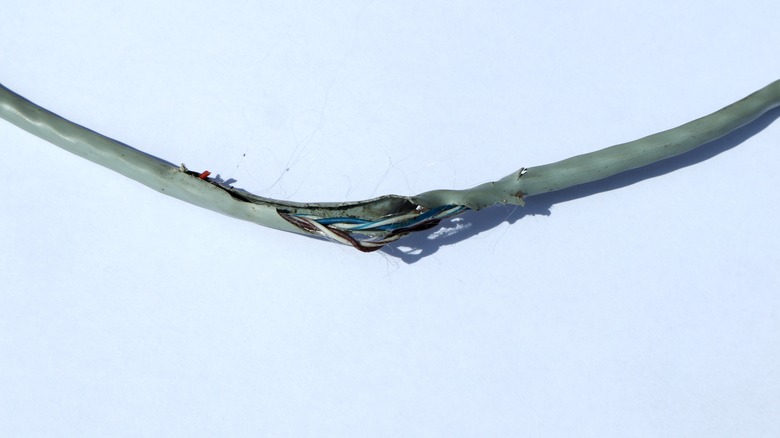
If your ethernet connection is underperforming, the first thing you should do is unplug and inspect the cable. Check its entire length, as well as its connectors, for any obvious abnormalities such as tearing, nicks, or physical warping. If there's any kind of physical problem, then the cable is no longer ideal for your purposes and needs to be replaced.
If you're going out for a new cable, you should ensure you're getting the right kind of cable. If you had your old one for a long time, it might not be optimized for modern internet frameworks, which could slow your connection. Make sure to get at least a Cat5 cable or better to facilitate a proper connection.
If it's not the cable, the problem could also be with the ethernet ports on your computer or router. It's the same deal as inspecting the cable –- carefully check the ports for signs of warping, cracking, or other damage. Unfortunately, if the ports are damaged, you might need to get your device serviced, as that's much harder to replace or fix on your own.
How to fix software ethernet problems
Software problems are generally more of a Wi-Fi thing than an ethernet thing, but that doesn't mean they never happen. After all, your computer has separate network drivers for connecting via ethernet and Wi-Fi. If your Wi-Fi drivers are fine, but your ethernet drivers are out of date or busted, then obviously, your Wi-Fi isn't going to get a good connection.
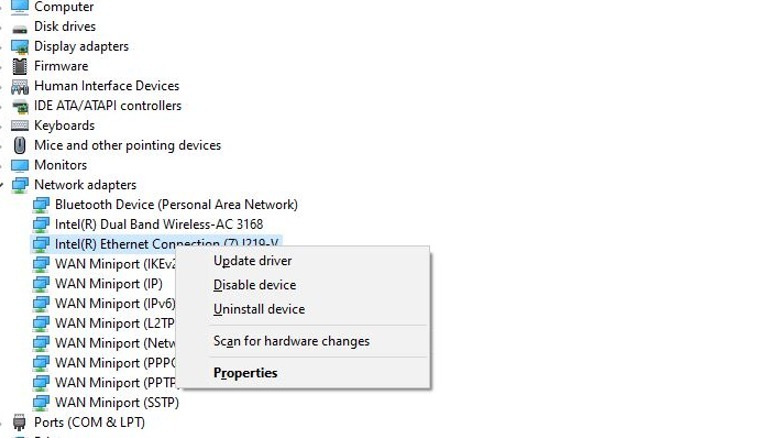
You can update your ethernet drivers via the Windows Device Manager.
-
Right-click on the Start button.
-
Select Device Manager.
-
Expand the Network Adapters category in the Device Manager.
-
Find your ethernet network adapter driver in the list. It should have the word "ethernet" in it.
-
Right-click on your ethernet driver and click Update driver.
-
Windows will scan for updates for the driver and download them if they're available.
-
Alternatively, right-click on your ethernet driver and click Disable driver to turn it off.
-
Wait a moment, then right-click on the driver again and click Enable driver to turn it back on.
It's also possible that the problem is on your router's end, meaning that it may need a firmware update. This, unfortunately, isn't something you can do from your Device Manager. Visit your internet provider's website for a guide on updating your router's firmware.