12 Weirdest Engines Ever Found In Production Cars
Production cars have come a long way since the invention of the combustion engine, and car manufacturers have always sought to innovate and push the limits of what is possible. An area of particular innovation has been in the design of car engines, as over the years there have been some truly strange and unusual engine designs used in production cars.
From the rotary engine of the Mazda RX-7 to the opposed-piston Achates Power block, these remarkable machines all have unique features that set them apart from traditional engines. While some of these engines were short-lived and never caught on, others continue to be used today in production cars. These engines represent the creativity and innovation of car manufacturers and are a testament to the ongoing evolution of automotive technology.
Despite the challenges they faced, these engines have left their mark on the automotive industry and helped to push the boundaries of what is possible in engine design. In this list, we'll explore 12 of the strangest engines ever used in production cars, the cars that housed them, and the impact they had on the automotive industry.
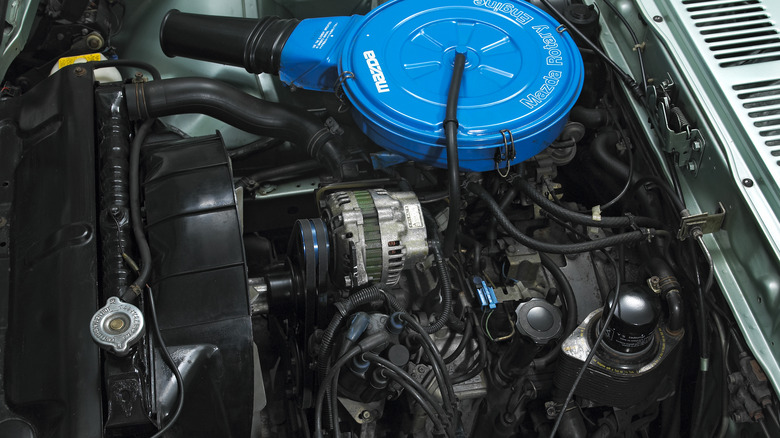
Wankel engine
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that has a rotary design instead of the traditional piston and cylinder setup. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel in the 1950s and has since been used in a number of vehicles, most notably the Mazda RX-7 and RX-8 sports cars.
Unlike traditional engines, which use reciprocating pistons to convert fuel into energy, the Wankel engine uses a rotor with a triangular shape that rotates around a fixed center housing. This design allows for a high power-to-weight ratio, smoother operation, and a smaller size compared to traditional piston engines. However, it also has some disadvantages such as high fuel consumption and potential sealing problems due to its unique shape.
Despite these challenges, the Wankel engine remains a unique and interesting alternative to traditional piston engines. Its simple design allows for fewer moving parts, which can reduce maintenance costs and increase reliability. However, its unique shape can also make it difficult to design effective seals, which can cause issues with fuel efficiency and emissions.
Overall, the Wankel engine represents a fascinating example of innovation in engine design. While it may not be as widely used as traditional piston engines, it remains an interesting and viable alternative for certain applications, particularly in sports cars where the high power-to-weight ratio and smooth operation can be beneficial.
The opposed-piston engine
The opposed-piston engine is a unique internal combustion engine that employs two pistons per cylinder. The opposed-piston engine's pistons move towards each other to compress the fuel mixture, eliminating the need for a separate cylinder head. This design leads to higher thermal efficiency and lower emissions since there is less heat loss during combustion.
The Achates Power engine is a modern example of an opposed-piston engine. It is designed for heavy-duty applications such as commercial and military vehicles, where fuel efficiency and emissions are critical factors. While the opposed-piston engine has significant potential advantages, its complex design and manufacturing challenges have limited its widespread use in the automotive industry. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development are being conducted to improve this engine's performance and efficiency.
The main advantage of the opposed-piston engine is its ability to generate more power with fewer cylinders. This makes it an attractive option for applications where space and weight are limited, such as in airplanes and military vehicles. However, its unique design also poses challenges such as increased complexity and manufacturing costs. Overall, the opposed-piston engine represents a unique and interesting alternative to traditional engine designs, and further research and development could lead to its increased adoption in various applications.
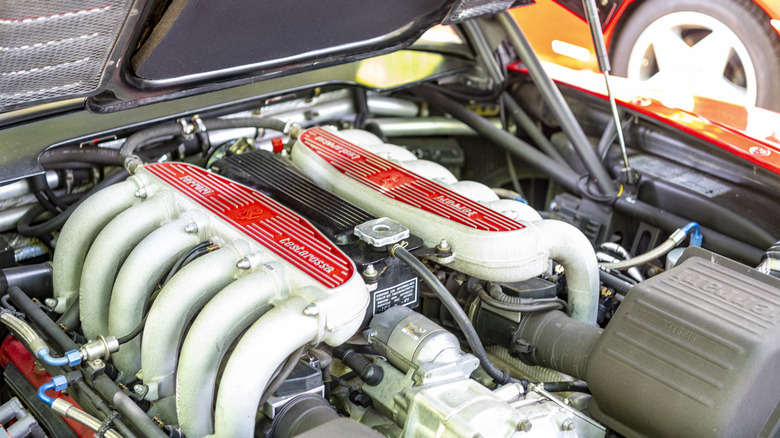
Flat-12 engine
The flat-12 engine is a unique type of internal combustion engine that has been used in some of the most iconic sports cars in automotive history. With 12 cylinders arranged in a V shape and a flat layout, the flat-12 engine has a lower center of gravity compared to other engine designs, which improves handling and stability. The engine's compact size also makes it a desirable option for high-performance cars where space is at a premium.
Perhaps the most famous car to use the flat-12 engine is the Ferrari Testarossa, which was produced from 1984 to 1996. The Testarossa's flat-12 engine was capable of producing up to 385 horsepower, which allowed the car to reach a top speed of 180 miles per hour. Another notable car to use the flat-12 engine was the Ferrari 512 BB, which was produced from 1976 to 1984. The 512 BB was a mid-engine sports car with a flat-12 engine producing up to 360 horsepower.
Despite its advantages, the flat-12 engine can be more complex and expensive to manufacture than other engine designs due to its unique layout. Additionally, the engine's location in the rear of the car can make it difficult to access and service, which can increase maintenance costs. However, the distinctive exhaust note and high power output make the flat-12 engine a favorite among enthusiasts and a symbol of high-performance sports cars.
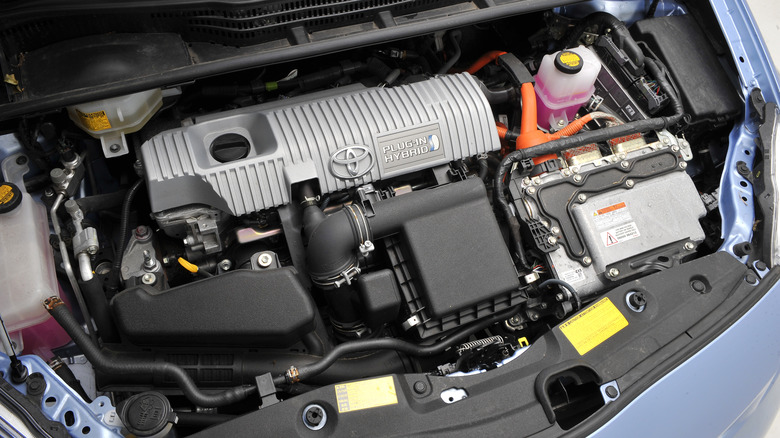
The hybrid engine
The hybrid engine is a type of powertrain that combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The Toyota Prius and Honda Insight are popular examples of cars that use a hybrid engine. The engine operates by using the electric motor to support the gasoline engine during acceleration or high-power demands and by utilizing regenerative braking to recharge the battery pack. This design allows the car to run more efficiently and quietly than a traditional gasoline engine while decreasing emissions and enhancing overall performance.
Despite its numerous benefits, the hybrid engine can be more complex and expensive than other engine designs, requiring specialized maintenance and repair. However, hybrid engines are becoming more prevalent in production cars and are a crucial aspect of the shift toward more sustainable transportation. The increasing focus on environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient vehicles has led to further innovation and development in hybrid engine technology, with automakers striving to produce more effective and efficient hybrid engines.
As a result, the hybrid engine remains a promising solution for reducing emissions and enhancing fuel economy, and it will likely continue to play a significant role in the automotive industry's efforts to reduce its environmental impact.
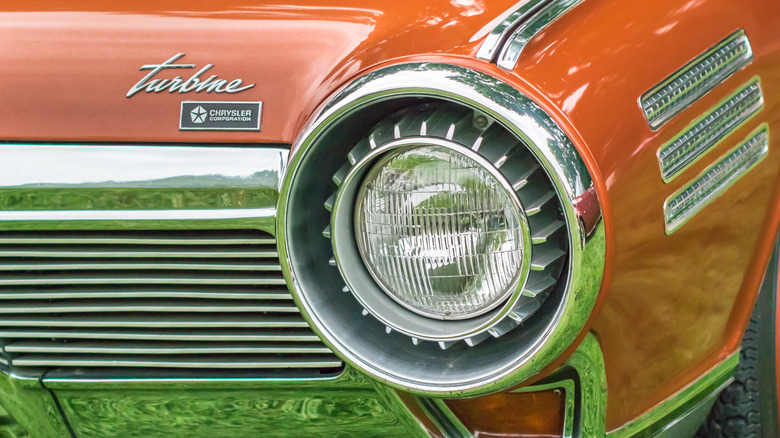
The turbine engine
The turbine engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a different approach to generate power compared to traditional combustion engines. It is known for its high power output, efficiency, and low emissions. Unlike traditional engines, which use pistons to convert fuel into mechanical power, the turbine engine uses a turbine to create power. The process starts with fuel being burned in a combustion chamber, producing hot gases. The hot gases are then directed towards a turbine, which drives a compressor to produce power.
The Chrysler Turbine Car, manufactured in the 1960s, was one of the few cars that used a turbine engine. However, the turbine engine has some drawbacks that have prevented it from becoming widely used in the automotive industry. One of the main issues is the high cost and complexity of the engine. Additionally, turbine engines require specialized maintenance and repair, which can be expensive.
Another challenge is the difficulty of regulating the engine's power output. Turbine engines can accelerate rapidly, leading to stability issues and making it challenging to achieve steady-state operation. Despite these challenges, the turbine engine remains a fascinating alternative to traditional combustion engines and is widely used in other industries, such as aviation and power generation. The turbine engine's unique approach to power generation continues to inspire innovation and research in the field of internal combustion engines.
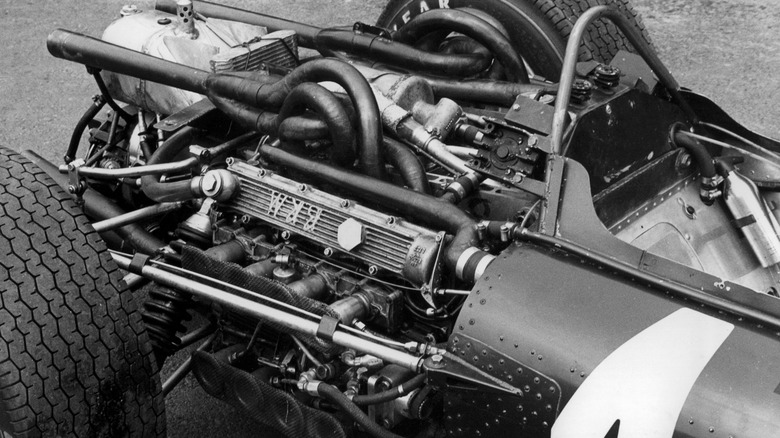
H-16 engine
The H-16 engine is an internal combustion engine that consists of 16 cylinders arranged in an H shape. This configuration is quite uncommon, with the BRM P83 race car being one of the few vehicles to use it. The H-16 engine was designed to maximize power output by combining the benefits of both V and horizontally-opposed engine layouts.
The H shape of the engine allowed for a more compact design while still retaining the power output of a larger engine. The BRM P83 was a highly innovative and advanced race car for its time, using the H-16 engine to achieve impressive performance on the track. However, the H-16 engine faced challenges in terms of reliability and performance, ultimately limiting its use and popularity.
Despite its limitations, the H-16 engine remains an interesting and unique example of engine design. Its unusual shape and configuration continue to captivate enthusiasts and engineers alike, as it represents a fascinating combination of different engine layouts. With continued innovation and development, the H-16 engine has the potential to offer even more exciting possibilities for high-performance applications in the future, while its rare and distinctive design ensures its place in automotive history.
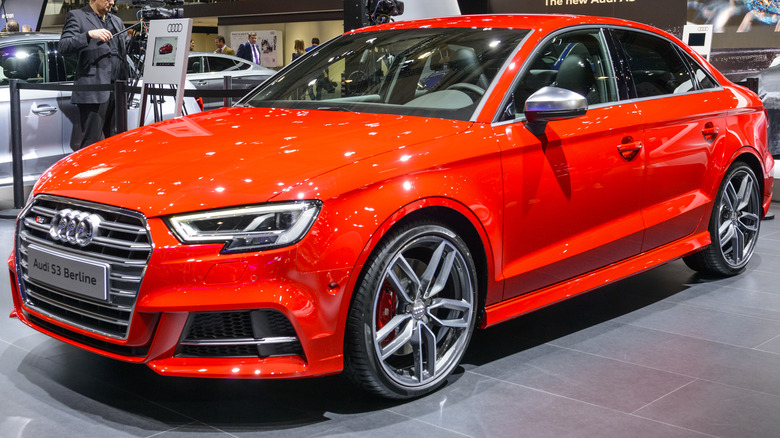
V-4 engine
The V4 engine is a lesser-known configuration of internal combustion engines, comprising four cylinders positioned in a V shape. While less common than the typical inline four-cylinder or V6 engines, it has been utilized in some production cars, including the Ford Taunus and Saab 96. The V4 engine is essentially a scaled-down version of the V6 engine, with two cylinders on each side of the V. This layout allows for a more compact design while maintaining the necessary power output.
One of the significant advantages of the V4 engine is better balance and smoother operation, resulting in less vibration and noise during the vehicle's operation. This engine layout also provides better fuel efficiency and acceleration, making it an ideal choice for small cars or other applications where space is limited. However, the V4 engine's complexity can increase manufacturing and service costs, making it less common in modern vehicles.
Despite its challenges, the V4 engine remains a fascinating and unique alternative to other engine configurations. Some automotive manufacturers continue to use it for small and midsize vehicles, such as the Audi S3 and Volkswagen Golf, taking advantage of its benefits while managing the complexity of its design. With advancements in technology, the V4 engine's limitations are becoming more manageable, and it is expected to remain a relevant engine configuration for the foreseeable future.
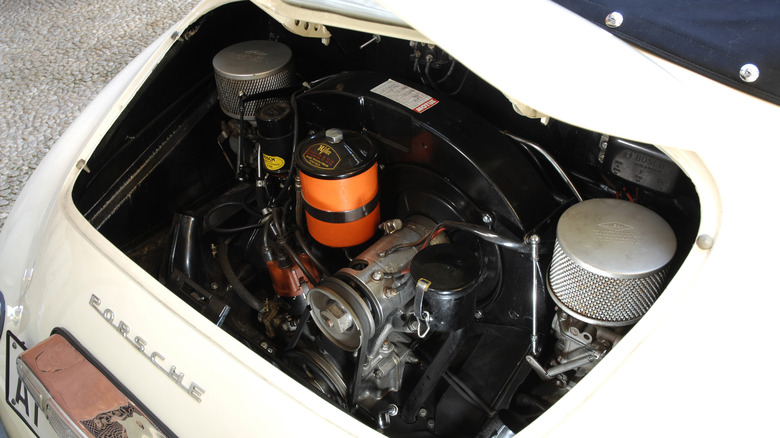
Flat-4 engine
The flat-4 engine, also known as the boxer-four or horizontally opposed-four engine, is a fascinating configuration with a distinct appearance and unique performance characteristics. This engine layout features four cylinders arranged in a flat configuration, mounted in two rows on opposite sides of the crankshaft, resembling a boxer's fists. The flat-4 engine is most commonly associated with Subaru and Porsche vehicles, such as the Subaru FB series engine and the Porsche 356.
One of the main advantages of the flat-4 engine is its low center of gravity, which helps improve handling and stability. Additionally, this engine configuration provides good weight distribution, making it ideal for use in rear-wheel-drive or all-wheel-drive vehicles. The flat-4 engine also delivers smooth power delivery due to its balanced design and has a unique sound that enthusiasts often find appealing.
Despite its many advantages, the flat-4 engine can have some drawbacks, such as limited space for specific engine components due to its compact design. This can make it challenging to perform maintenance or repairs. However, advancements in technology have helped overcome many of these challenges, making the flat-4 engine a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
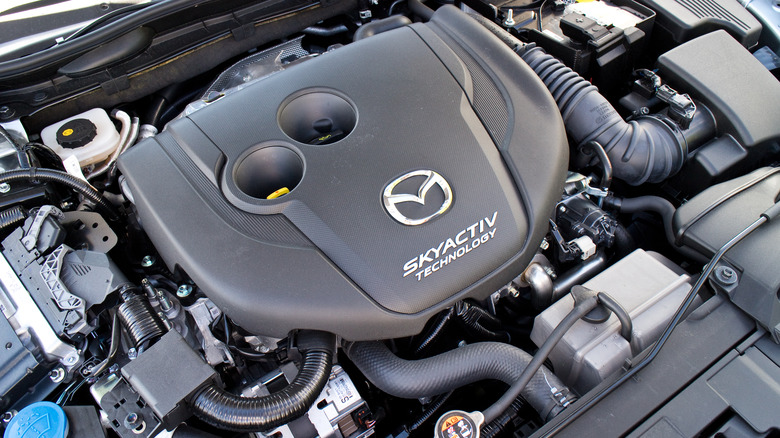
HCCI engine
The HCCI engine, which stands for homogeneous charge compression ignition engine, is a type of internal combustion engine that offers a combination of compression and spark ignition for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder. This process results in a more efficient combustion process and can lead to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions. One notable example of an HCCI engine is the Mazda Skyactiv-X, which uses a spark-controlled compression ignition system that combines spark ignition with compression ignition. This technology allows for better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
HCCI engines are becoming more popular as they offer the potential for higher fuel efficiency and lower emissions, making them a promising technology for the future of internal combustion engines. Although HCCI engines are still in the development phase, they offer a potential alternative to traditional gasoline engines and could help reduce the carbon footprint of transportation in the years to come. By providing a more efficient combustion process, HCCI engines could help decrease the amount of fuel consumed while reducing harmful emissions. As a result, many car manufacturers are investing in HCCI engine technology as they look for ways to create more environmentally friendly vehicles.
The radial engine
The most significant advantages of radial engines are their compact size and lightweight design relative to their power output. Compared to traditional piston engines, radial engines have a simpler design with fewer moving parts. This feature allows them to operate more smoothly and quietly. Another unique characteristic of radial engines is their power delivery, which many drivers find appealing. The engine's high-revving capabilities, combined with its distinctive sound, make it an attractive option for performance enthusiasts.
However, rotary engines have some drawbacks, including relatively poor fuel efficiency and high emissions compared to other engine types. They are also known to be less reliable than piston engines because their seals can wear out over time, leading to issues with compression and oil consumption.
Despite these challenges, radial engines continue to be popular in certain applications, particularly in high-performance vehicles and sports cars. Mazda has been a pioneer in rotary engine technology, producing a series of rotary-powered sports cars such as the 13B and RX-8. Though Mazda discontinued the production of rotary engines, enthusiasts still maintain a strong interest in this unique engine type in the automotive industry.
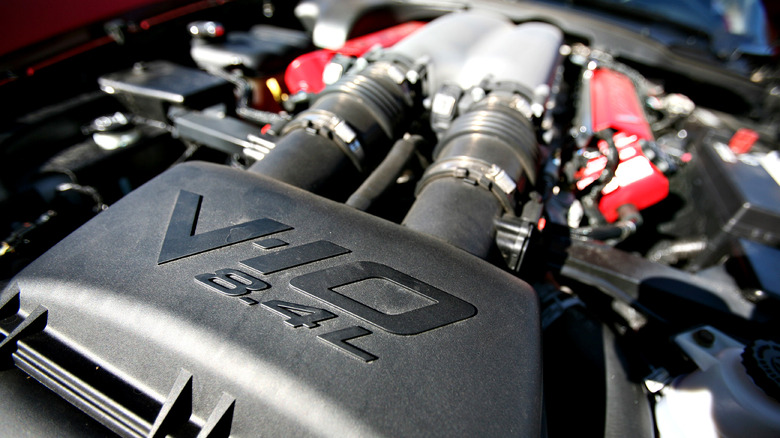
V-10 engine
The V10 engine has a rich history in the world of high-performance sports cars, and one of the most notable examples of a V10-powered vehicle is the Dodge Viper. The Viper was first introduced in 1992 and quickly gained a reputation as a powerful and aggressive American sports car. The V10 engine was a key part of the Viper's appeal, delivering up to 645 horsepower in its most powerful iteration.
The Viper's V10 engine has a displacement of 8.4 liters and features a unique design with two valves per cylinder and a pushrod valvetrain. This design helps to reduce the engine's weight and complexity, making it more suitable for high-performance applications.
In addition to the Dodge Viper, the V10 engine has been used in a number of other high-performance sports cars, including the Audi R8, Lamborghini Gallardo, and Porsche Carrera GT. These vehicles are known for their impressive acceleration and top speeds, as well as their distinctive engine notes.
While the V10 engine may not be as common in mainstream passenger cars, it remains a popular choice for enthusiasts and an important part of automotive history. Its unique sound, high power output, and impressive performance capabilities make it a favorite among sports car fans around the world.
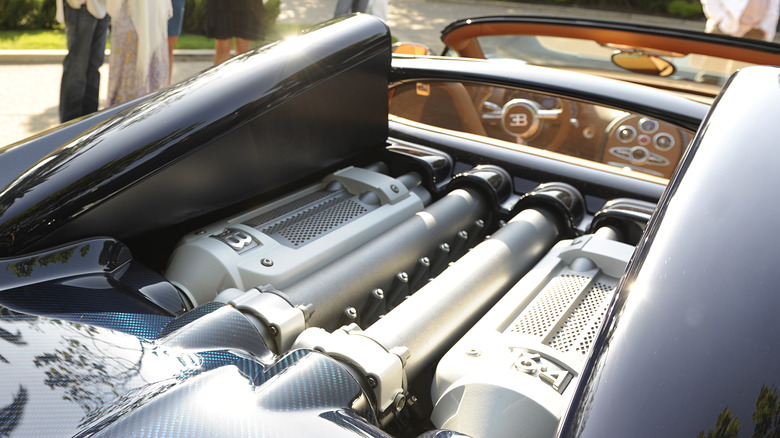
V-16 engine
The V16 engine is a rare and prestigious engine configuration, with only a few select vehicles throughout history utilizing this layout. This engine is considered a symbol of luxury, prestige, and high performance, due to its power output and high level of refinement.
The V16 engine was first introduced in the early 1930s and was used in some of the most high-end luxury cars of the time, such as the Cadillac V-16 and the Marmon Sixteen. These vehicles were known for their exceptional power and smooth operation, which made them popular among wealthy individuals and dignitaries.
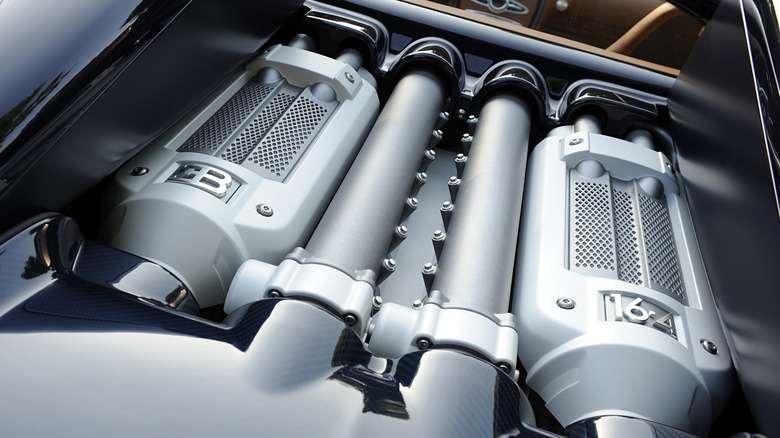
Today, the V16 engine is not commonly used in mainstream production cars due to its high manufacturing costs and complexity. However, it remains a popular choice for high-end luxury vehicles, supercars, and concept cars. One notable example is the Bugatti Veyron, which was one of the fastest and most powerful production cars ever made. Another example is the Rolls-Royce Vision Next 100 concept car, which features a futuristic V16 engine powered by an advanced electric propulsion system.
The V16 engine typically has a displacement of around 8.0 to 10.0 liters or more and can produce up to 1000 horsepower or more in some applications. The engine's high power output and smooth operation make it ideal for use in high-end luxury cars and high-performance vehicles, although it is quite rare and expensive to produce.