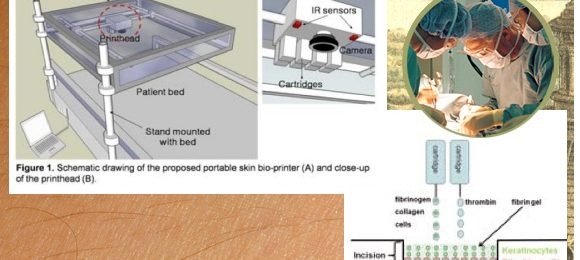
Printer Cartridges Full Of Living Tissue
This is no horror movie, this is part of a recent presentation at the American College of Surgeons Clinical Congress, where Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine researchers had a super fun time showing off their results from a printer that uses living cells instead of ink. Fluid based inkjet technology used in the very printers you've got in your home or office is used to lay down cells, printing large sections of living tissue down on cut up or damaged areas of the body.
These fine folks from the Institute note that "any loss of full-thickness skin of more than 4 cm in diameter will not heal by itself," and that with this device, (refined and tested extensively, of course,) skin that might have been otherwise damaged horrifically can now be patched up to a much higher level of healthiness. Testing has occurred on mice revealing advanced healing by the second and third week of recovery and complete closure of the skin by the end of week three on wounds that would otherwise still be open to infection.
The printer works with two heads, one that dispenses skin cells mixed with fibrinogen (a blood coagulant) and type I collagen (connective tissue's main component in scars), the other which sends out thrombin (another coagulant.) Together these create a chemical reaction and form fibrin, another protein that works on the clotting of blood. On top of this is one more layer printed by the printer: keratinocytes – the outer layer of skin we've all got right this moment.
Future research will be done on the pigs who, if you know your Gangs of New York lore, are great to practice stabbing on because they've got skin that very closely resembles human skin. Will this device ever hit your local wartime hospital or town hospital? Who can tell?
It'd certainly be great for my future kid or kids to be growing up knowing that when they flip over their bike handlebars, that their scun-up knees will be able to be printed out at the local doc-shop. Maybe in fun new colors? CMYK! Check out more information about the presentation over at the website for Clinical Congress.
[Via Technology Review]